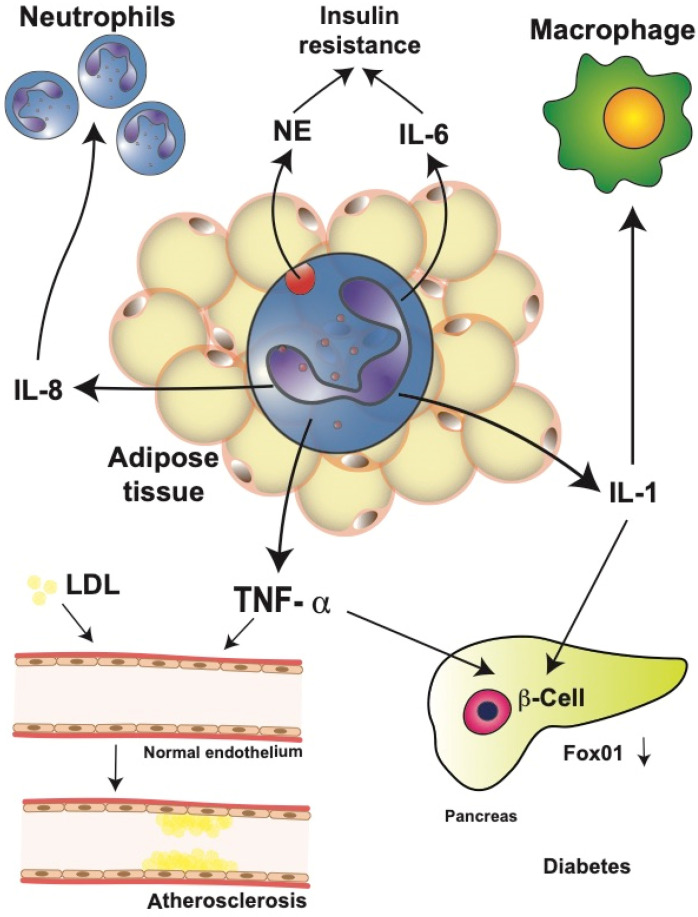
Figure 5.
Neutrophils in obesity-related complications. Neutrophils in obese adipose tissue release large amounts of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). These cytokines have important systemic effects leading to obesity-related complications. IL-8 recruits more neutrophils into the adipose tissue, creating an amplification cycle. Neutrophil elastase (NE) and IL-6 contribute to the development of insulin resistance by impairing insulin signaling. IL-1β is an important activator of macrophages in multiple parts of the body. Furthermore, IL-1β, together with TNF-α in pancreatic islets, induces β cell dedifferentiation by downregulating transcription factor Fox01, which regulates β cell proliferation. Together, these events may result in type 2 diabetes mellitus. In addition, TNF-α can alter the adhesion function of endothelial cells by inducing increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL) uptake. These changes have been associated with the progression of atherosclerosis.