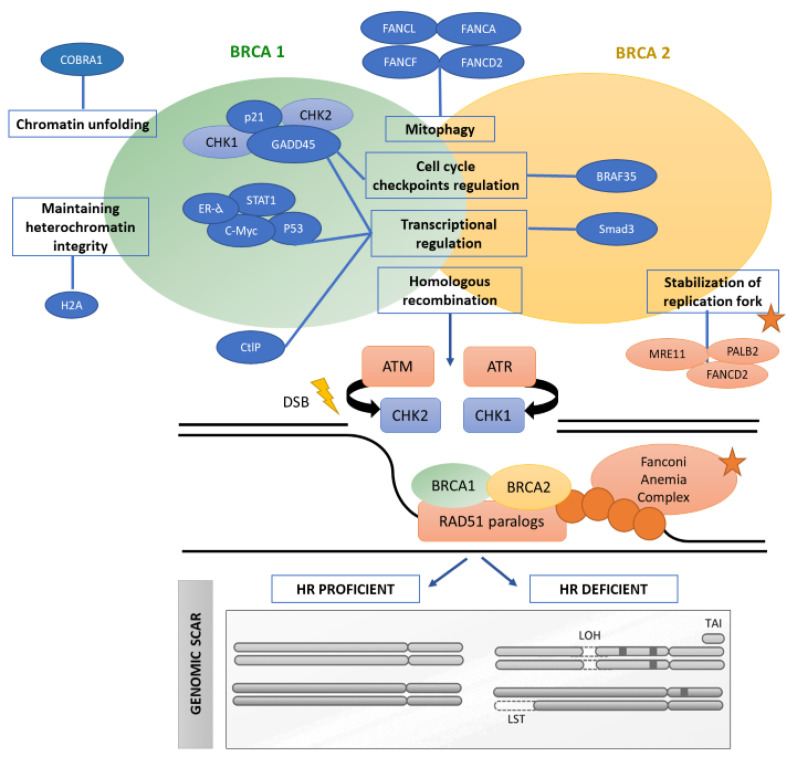
Figure 1.
Functional features of proteins involved in HRD. Adapted with permission from Gorodetska et al. [7], copyright 2019 the authors, Ivyspring International Publisher under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/, accessed on 12 May 2022) and Hoppe et al. [6], copyright 2018 by the authors published by Oxford University Press. The figures have been modified for the purposes of this review. Proteins involved in the HR system have functions in DNA repair, but also participate in cell cycle regulation, transcriptional activation and chromatin remodeling. Genomic scarring is defined by the presence of chromosomal abnormalities related to HRD: (a) telomeric allelic imbalance (TAI) due to inappropriate chromosomal end fusions because of aberrant end joining, (b) loss of heterozygosity (LOH) related to inaccurate repair of sister chromatids during the S/G2 cell cycle phase and (c) large-scale transitions (LSTs) that are chromosomal breaks of more than 10 Mb.