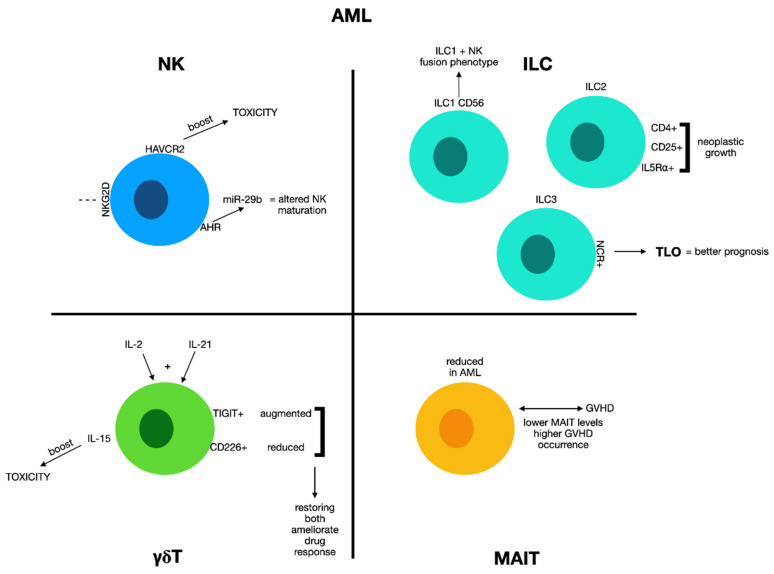
Figure 1.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) unconventional immune cell scenario. NK: The NK receptor NKG2D can make tumor cells vulnerable to NK cell-mediated lysis. The systemic reduction of NKG2D on the NK surface of tumor subjects is reported, causing an alteration in NKG2D-mediated NK cell function. Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 (HAVCR2 or TIM-3) is intensely present on NK cells in AML subjects, associated with augmented cytotoxic activity and with a better prognosis. Moreover, AML blasts can stimulate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) system that augments miRNA-29b production in NK cell precursors, altering their maturation process and activity. ILC: The CD56 innate cell set has mixed phenotypic and transcriptional characteristics of traditional ILCs and lytic NK cells. These CD56 ILC1-like cells have a relevant cytotoxic ability. On the other side, the co-transfer of CD4+CD25+IL5Rα+ILCregs stimulates neoplastic growth. Finally, the presence of NCR+ ILC3 in TLO is related to a better prognosis. γδ T: Results indicate an altered presence of TIGIT and CD226 on γδ T cells with an increase in TIGIT+ γδ T cells and a reduction in CD226+ γδ T cells in subjects with de novo AML, but restoring both can ameliorate a drug response. IL-2 and IL-21 stimulate γδ T cells and IL-15 boosts it toxicity. MAIT: A reduction in AML. In addition, lower MAIT levels favor higher GVHD occurrence.