Table 3.
Structure and mechanism of hRR subunit inhibitors.
| Structure | Name | RR Subunit Targeted | Mechanism of RR Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|
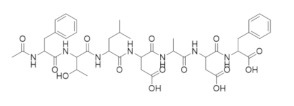
|
P6 | RR1 | Prevents binding of the RR2 subunit |
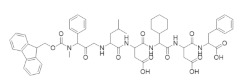
|
P7 | RR1 | Prevents binding of the RR2 subunit |
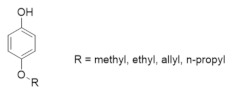
|
p-Alkoxyphenols | RR2 | Quenches the tyrosyl radical |
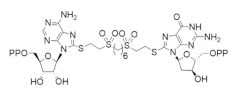
|
ADP-S-HBES-S-dGTP | RR1 | Targets the S-site |
|
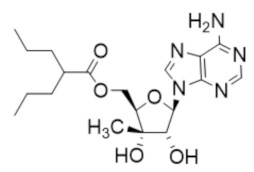
A167 | RR1 | Compeites with ATP to bind the A-site |
|
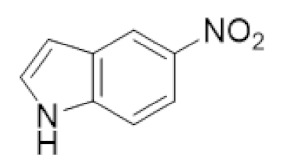
5-NITP | RR1 | S-site inhibitor that prevents RR1 hexamerization |
|
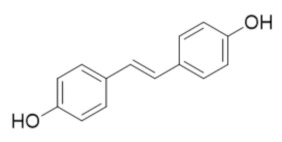
DHS | RR2 | Induces degradation of RR2 proteosome degredation pathway |
|
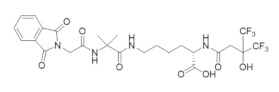
OxolsolndoLys | RR1 | Induces formation of inactive a6 hexamers |
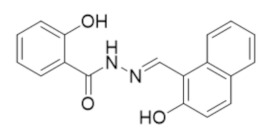
|
NSAH | RR1 | Reversible C-site inhibitor |
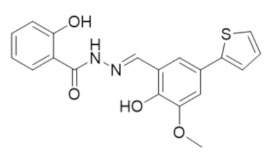
|
TP6 | RR1 | Reversible C-site inhibitor |
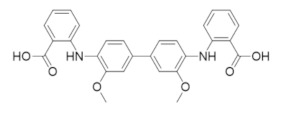
|
NSC73735 | RR1 and RR2 | Prevents alpha subunit hexamerization and quenches the tyrosyl radical of RR2 |
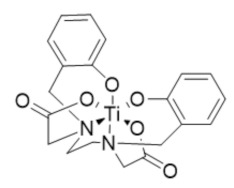
|
Ti(HBED) | RR2 | Depletes intracellular labile iron pools by transmetalation |
|
Ti(Deferasirox)2 | RR2 | Depletes intracellular labile iron pools by transmetalation |
