Figure 3.
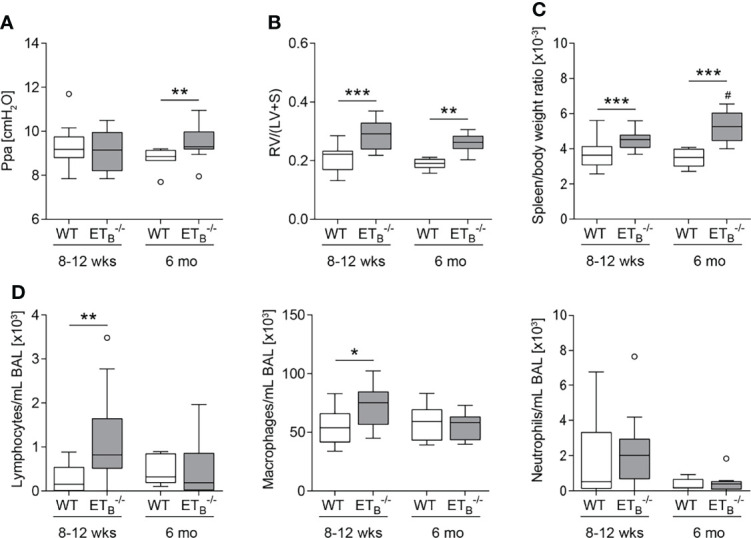
ETB deficiency was age-dependently associated with increased pulmonary arterial pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy, splenomegaly, and increased number of lymphocytes in bronchoalveolar lavage. Lungs, hearts, and spleens of 8- to 12-week (wk)-old and 6-mo-old rescued endothelin B receptor-deficient (ETB -/-) and corresponding wild-type (WT) mice were removed, or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed. (A) In isolated perfused and ventilated lungs, under basal conditions, pulmonary arterial pressure (Ppa) was increased in 6-mo-old ETB -/- compared to WT mice of the same age. (B) Fulton index [ratio of right ventricle (RV) and left ventricle (LV) including septum (S)] determined after weighing the cardiac compartments was higher in ETB -/- compared to WT mice. (C) Determination of spleen weight related to body weight revealed splenomegaly in ETB -/- mice. (D) Analysis of differentially quantified leukocytes in BAL revealed increased number of lymphocytes and macrophages in BAL from 8- to 12-wk-old ETB -/- vs. WT mice of the same age. Data are represented as box plots depicting median, quartiles, and ranges excluding outliers (open circles). In (A–C), N = 7–28; in (D), N = 7–17. # indicates significant difference in the 6-mo-old vs. the corresponding 8- to 12-wk-old group, * indicates significant difference between ETB -/- vs. the corresponding WT group. */# p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Mann–Whitney U test).
