Figure 3:
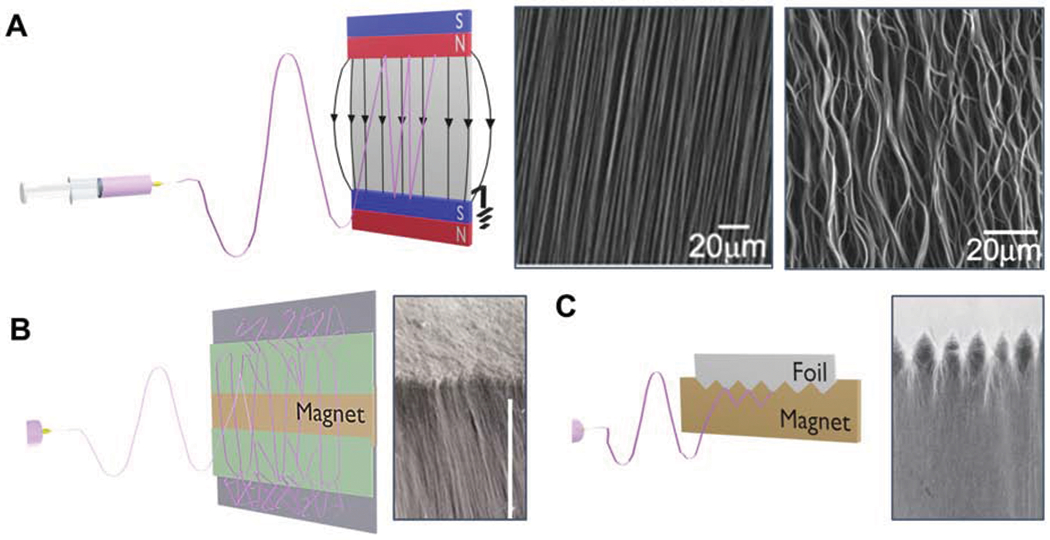
The use of magnetic electrospinning to produce anisotropic constructs with mechanism and alternative setups. A) Magnetic field-assisted electrospinning uses a conventional electrospinning setup with the addition of two parallel-positioned permanent magnets. An applied magnetic field results in highly aligned fiber deposition between the two magnets. Tortuosity may be introduced into aligned fibers by modulating the electrospinning flow rate. Reprinted with permission from Liu et al.72 Copyright 2010, Wiley-VCH GmbH, Weinheim. B) Alternate magnet configurations resulting in fiber alignment gradients from aligned to semi-aligned to random. Reprinted with permission from Tindell et al.77 Copyright 2020,Tindell et al. C) Interdigitated interfaces can be obtained through alterations in magnet configuration. Reprinted with permission from Tindell et al.77 Copyright 2020, Tindell et al.
