Figure 4.
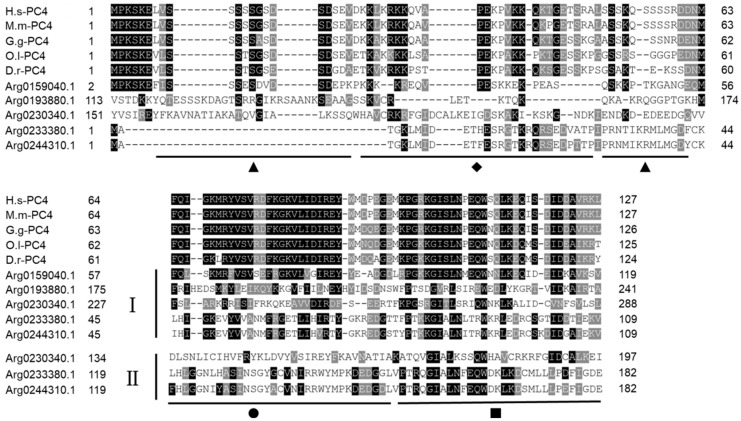
Multiple sequence alignment of AiPC4s from H. sapiens (H.s-PC4), M. musculus (M.m-PC4), G. gallus (G.g-PC4), O. latipes (O.l-PC4) and D. rerio (D.r-PC4) downloaded from NCBI. Amino acid residues that are conserved in at least 70% sequences can be stained. Conserved amino acid residues are shaded in black. The gray-shaded regions represent similar amino acid residues. Gaps are represented by dashes to improve the alignment. The ▲ represents the serine-rich region, ◆ represents the lysine-rich region, ● represents the ssDNA-binding region and ■ represents the dimerization region. I and II represent the first and the second PC4 domain in AiPC4s, respectively. Accession numbers of other species’ PC4s are listed in Table S1.