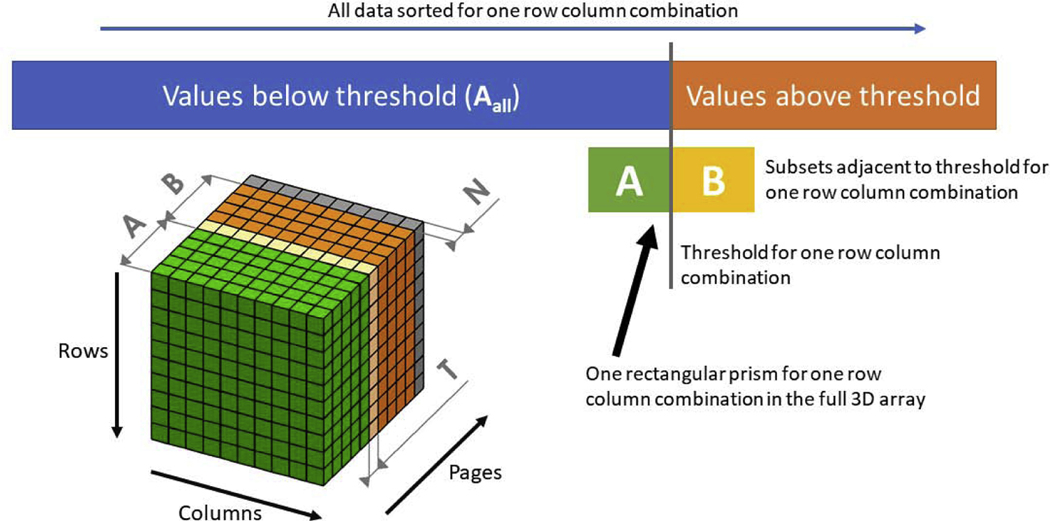
Figure 1:
Structure of the 3D array ABN used in the efficient threshold algorithm. Each voxel contains a coherence value and the values are increasing in the direction of increasing page number. All coherence values below the threshold make up the conceptual array Aall, this array is never stored in its entirety, but only its subset A. The 2D array nAall is stored and contains the length of the conceptual Aall for each row and column combination. A and B contain the coherence sample subsets adjacent to the desired percentile. The threshold 2D array (T) is the first element in the sorted B set. The cube shows the implementation of the A, B, and N sets in a 3D array. The rows and columns are the time and frequency dimensions while the page dimension is coherence value samples. The last page of ABN is a null page (N) that contains a new coherence sample at each iterative step of the proposed algorithm.