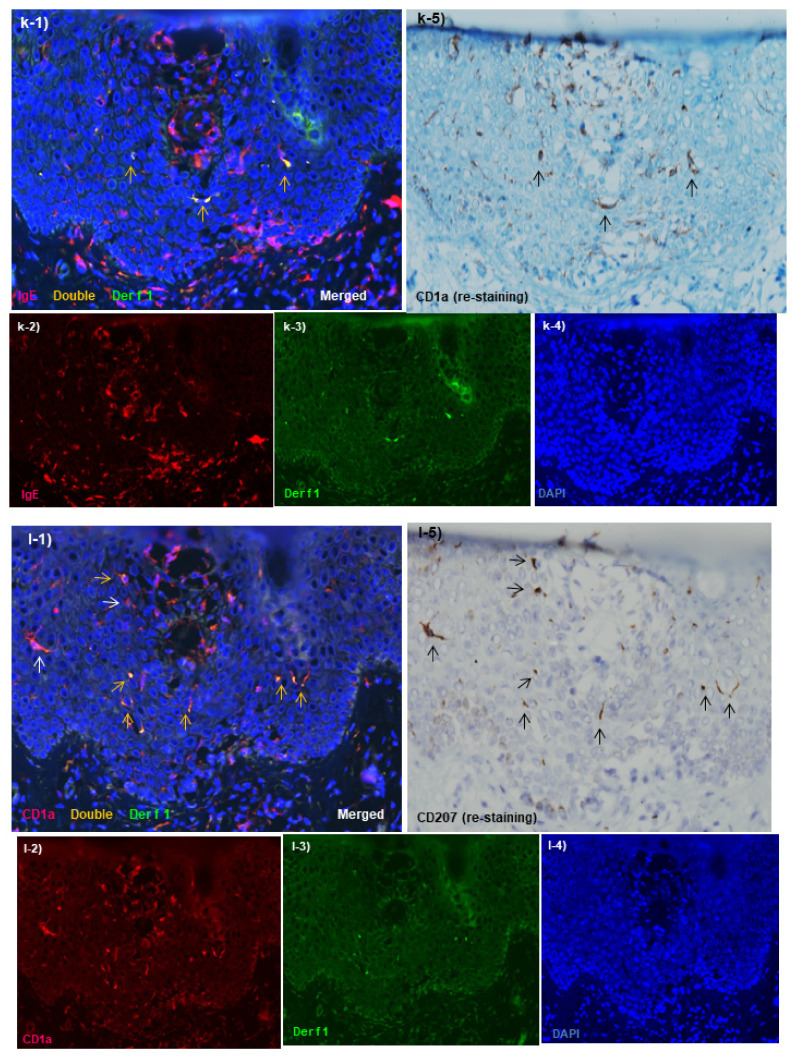
Figure 3.
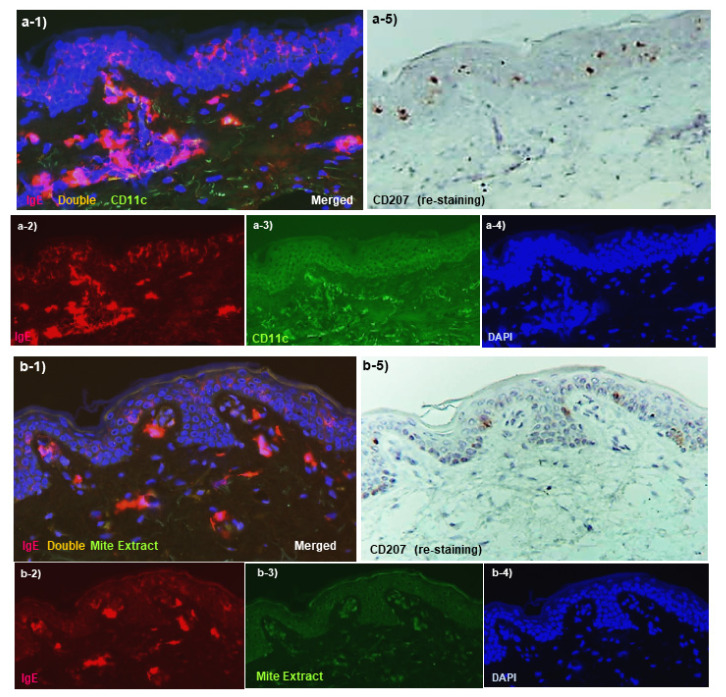
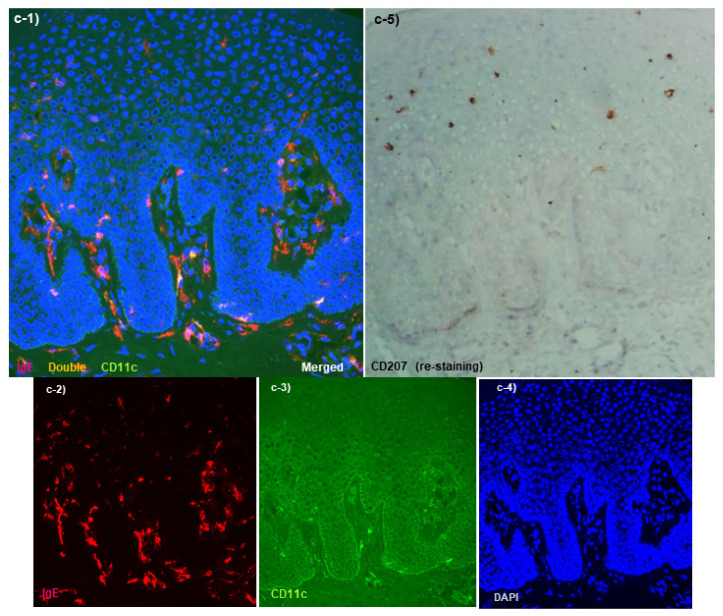
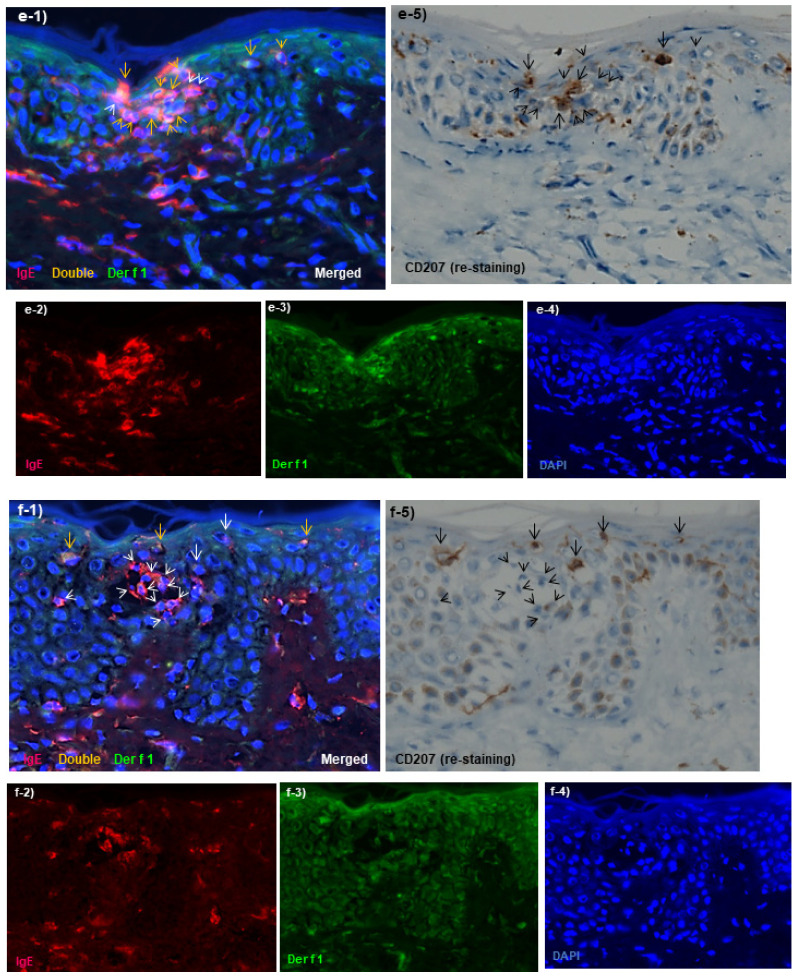
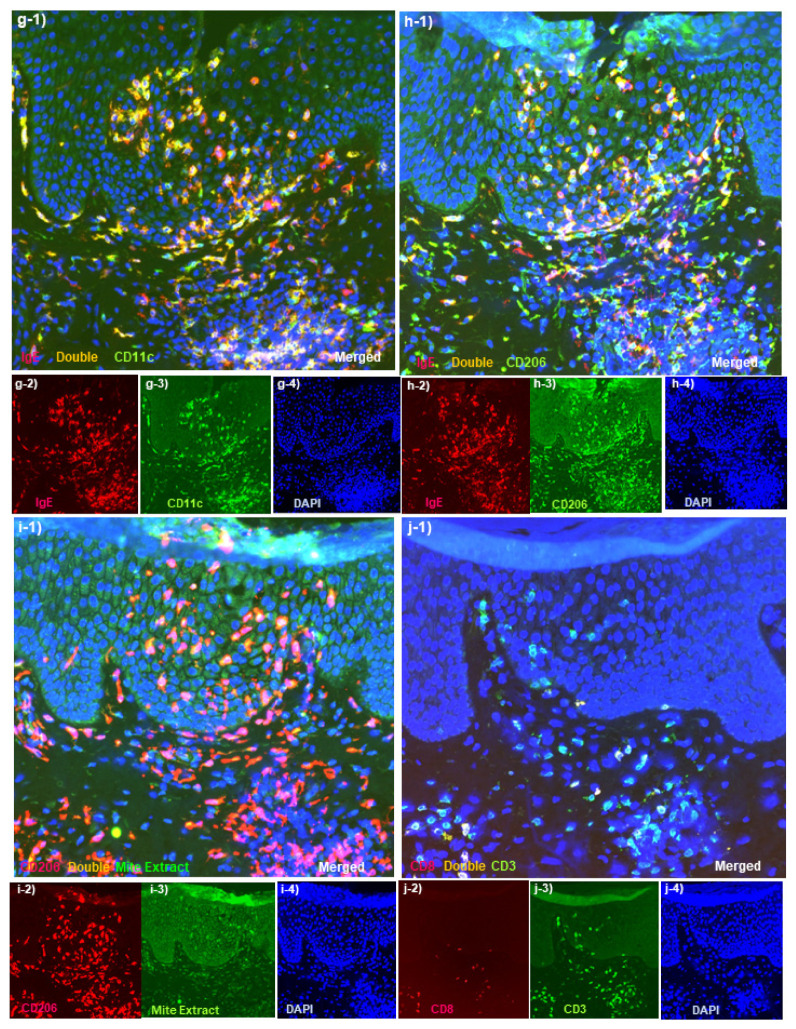
Immunohistopathology of skin manifestations of IgE-allergic AD. (a). Uninvolved skin: Regularly arranged IgE+ CD207+ LCs (red images of a-1 that colocalize with brown images of a-5), but not infiltrated IgE+ CD11+ IDECs (yellow image of a-1), are observed in the epidermis. Infiltration of IgE+ CD11+ inflammatory DCs (yellow images of a-1) in the upper dermis is slight. Note that the dendrites of LCs are not stained with CD207 (a-1,a-5).(b). Uninvolved skin: Few HDM antigens captured by IgE + LCs in the epidermis and by IgE+ infiltrating cells in the upper dermis are observed. (c). Lichenified eczema; non-spongiotic dermatitis: In the epidermis, IgE+ CD207+ LCs (red images of c-1 that are colocalized with the brown images of c-5) are located in the upper-middle layer, and IgE+ CD11+ IDECs (yellow images of c-1) are located in the lower layer. LCs without IgE expression (brown images of c-5 that are not colocalized with the red images of c-1) are also observed in the epidermis. (d). Lichenified eczema; non-spongiotic dermatitis: Most of the HDM antigens found in the epidermis are captured by IgE+ LCs (yellow images of d-1 that are colocalized with the brown images of d-5, arrows). An IgE+ LC that captured HDM antigens by extending a dendrite to the tight junction side is also observed (thick arrows in d-1 and d-5). Minimal lymphocyte infiltration is observed around these HDM antigen-capturing LCs. HDM antigens are also captured by IgE-expressing infiltrating cells, which are different from LCs, in the papillary and upper layers of the dermis (yellow images of d-1 that are not colocalized with the brown images of d-5 in the papillary and upper dermis). (e). Atopy patch test; an early lesion of focal spongiosis: Focal spongiosis shows an agglomerate infiltrated by IgE+ CD207+ LCs (arrows in e-1 and e-5) and IgE+ CD207− DCs (IDECs) (arrowheads in e-1 and e-5). In this agglomerate, both IgE+ LCs that captured HDM antigens (Der f1) (yellow images of e-1 that are colocalized with the brown images of e-5, yellow arrows) and IgE+ IDECs that captured HDM antigens (yellow images of e-1 that are not colocalized with the brown images of e-5, yellow arrowheads) are observed. (f). Atopy patch test; spongiotic vesicle: Inside the spongiotic vesicle, IgE+ CD207− DCs (IDECs) (red images of f-1 that are not colocalized with the brown images of f-5, white arrowheads) form an agglomerate, but HDM antigens (Der f1) captured by these cells are rarely observed. In the peripheral areas of the spongiotic vesicle, IgE+ LCs that captured HDM antigens (yellow images of f-1 that are colocalized with the brown images of f-5, yellow arrows) are observed. (g–j). Lichenified eczema; spongiotic dermatitis: IgE+ CD11+ IDECs infiltrate and aggregate in focal spongiosis (yellow images in the epidermis of g-1). IgE+ CD206+ IDECs infiltrate and aggregate in focal spongiosis (yellow images in the epidermis of h-1). Most of the IgE+ CD206+ IDECs that infiltrate in focal spongiosis capture HDM antigens (Mite extract) (yellow images in the epidermis of i-1). Accompanying infiltration of CD3+ CD8− (CD4+) T cells is mainly seen in this focal spongiosis (green images in the epidermis of j-1). (k,l). Lichenified eczema; spongiotic dermatitis that forms a spongiotic vesicle: Inside the spongiotic vesicle, IgE+ CD1a+ CD207− DCs (IDECs) form an agglomerate (red images in the center of the epidermis in k-1,l-1), but HDM antigens (Der f1) captured by these cells are rarely observed. IgE+ CD1a+ CD207+ LCs (arrows in k-1,k-5,l-1,l-5) are found around the spongiotic vesicle, and some of these cells captured HDM antigens (Der f1) (yellow arrows in k-1,l-1). Original magnifications: 200×, (a-l). In double immunofluorescence staining, nuclei are labeled with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue images). The images (f–i,k,l) are reproduced with permission from the authors and journals (Dermatopathology and Dermatology Clinics and Research) [76,86]. Characteristics of the patients shown the figures: the 61-year-old woman, (a–d,g–j); and the 84-year-old man, (e,f) were the same patients described in Figure 2; and the patient was a 71-year-old man with an elevated serum total IgE level of 2413 IU/mL and specific IgEs for Der f (k,l). Atopy patch test was carried out using allergen extracts of Der f [86]. The primary polyclonal antibodies against HDM antigens were mite extract (mite crude extract containing antigens from Der f and Der p) and Der f1 (the primary allergenic component of Der f that cross-reacts with Der p1) [76]. Abbreviations: AD, atopic dermatitis; CD, cluster of differentiation; Der f, Dermatophagoides farinae; Der p, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; DC, dendritic cell; HDMs, house dust mites; IDEC, inflammatory dendritic epidermal cell; IgE, immunoglobulin E; LC, and Langerhans cell.