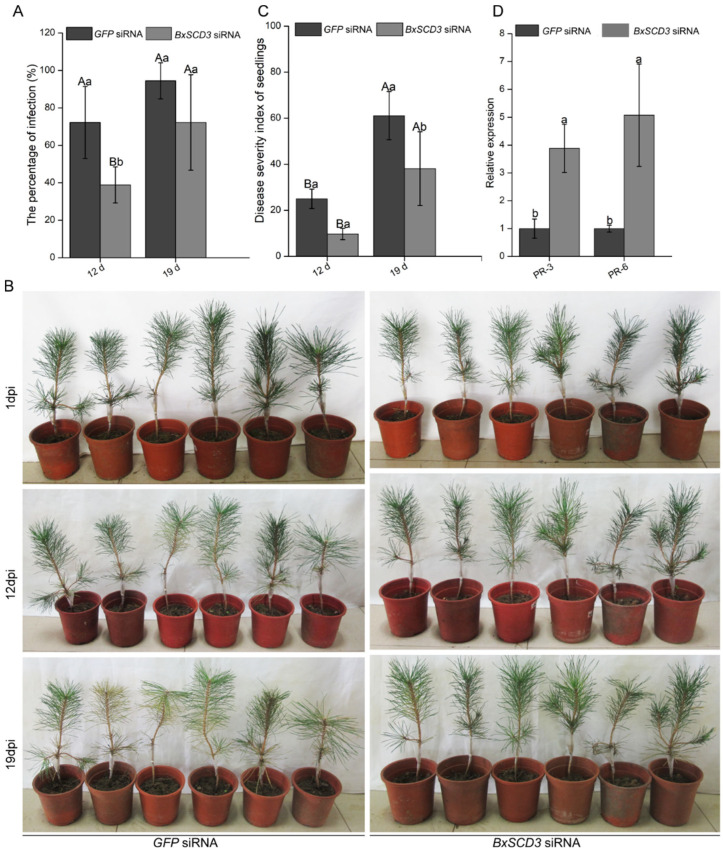
Figure 6.
BxSCD3 contributes to the virulence of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and inhibits the expression of defense-related genes in Pinus thunbergii. (A) The infection ratio of pine seedlings were calculated at 12 and 19 days post-inoculation (dpi). Three independent experiments were performed, and 18 individual P. thunbergii seedlings were used for each treatment. Data are the means, and the error bars represent ± SD from three biological replicates. Different letters on top of the bars indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, t-test) as measured by Duncan’s multiple range test. (B) The symptoms of P. thunbergii at 12 and 19 dpi with two different nematode treatments (BxSCD3 siRNA and GFP siRNA). (C) The disease severity index of pine seedlings were calculated at 12 and 19 days dpi. Data are the means, and the error bars represent ± SD from three biological replicates. Different letters on top of the bars indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, t-test) as measured by Duncan’s multiple range test. (D) The relative expression levels of pathogenesis-related genes PtPR-3 and PtPR-6 in P. thunbergii infected with BxSCD3 siRNA-treated nematodes. The seedlings infected with GFP siRNA-treated nematodes were used as controls. Data are the means, and the error bars represent ± SD from three biological replicates. Different letters on top of the bars indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, t-test) as measured by Duncan’s multiple range test.