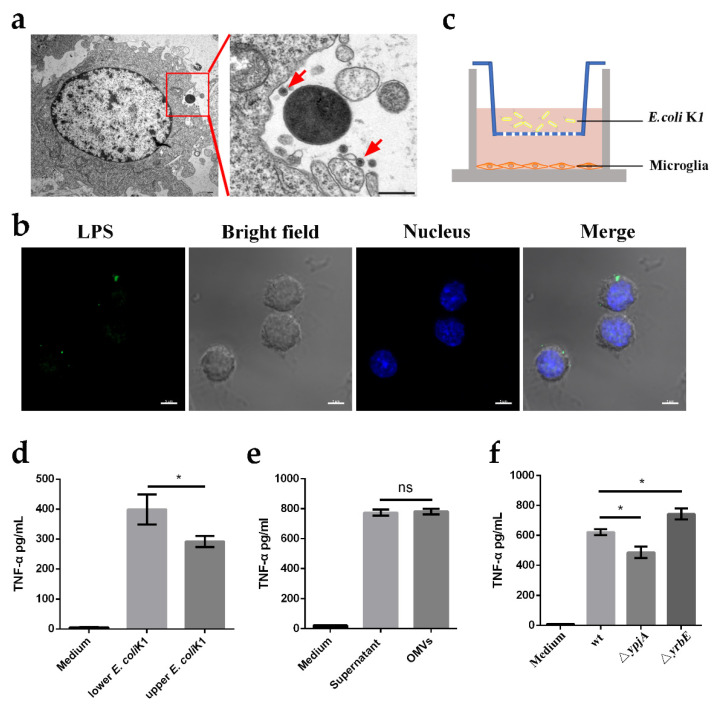
Figure 3.
Microglia recognize E.-coli-K1-derived outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) to release TNF-α. (a,b) Transmission electron microscopy (a) and confocal laser microscopy (b) were utilized to observe the secretion of OMVs by E. coli K1 when the bacteria were cultured with primary microglia. Images are representative of three independent experiments. High magnification image of red boxed area is shown on the right panel and red arrows indicate the observed OMV (a). Scale bars, 500 nm (a) and 20 μm (b). (c) Experiment scheme to determine the inflammatory activation of microglia by bacteria-secreted factors using Transwell plate. (d) ELISA analysis of TNF-α protein levels of BV2 microglia cell line incubated with wild-type E. coli K1 in the lower wells or upper wells. (e) ELISA analysis of TNF-α protein levels in microglia that were stimulated with bacterial supernatant or purified OMVs. (f) ELISA analysis of TNF-α protein levels in microglia that were cultured with wild-type E. coli K1, ΔypjA, or ΔyrbE. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3 independent experiments. p values were determined using Student’s t-test (d–f). * p < 0.05; ns, not significant.