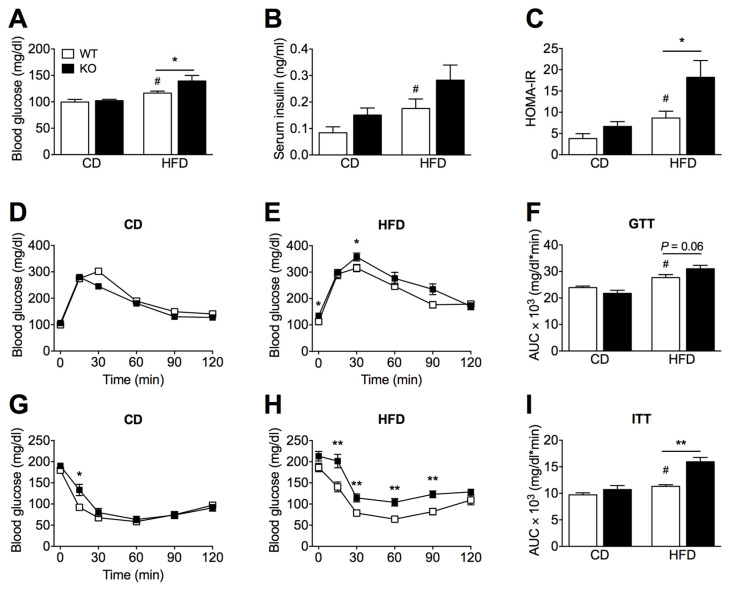
Figure 2.
Loss of SIRT2 exacerbates HFD-induced increase in blood glucose levels, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance. (A,B) Blood glucose levels (mg/dL) and serum insulin levels (ng/mL) of WT and SIRT2-KO mice fed a CD or a HFD at the end of the experiment measured after 15 h of fasting. (C) Insulin resistance score, HOMA-IR, is calculated as fasting plasma glucose times fasting serum insulin divided by 22.5. (D,E) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (ipGTT) was conducted in WT and SIRT2-KO mice after 24 days of CD or HFD feeding. Blood glucose levels of WT and SIRT2-KO mice at different time points after i.p injection of D-glucose (1.5 g glucose/kg body weight). (F) Average AUC of the ipGTT curves was calculated using the trapezoidal rule. (G,H) Intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test (ipITT) was performed in WT and SIRT2-KO mice fed a CD HFD after 28 days. Blood glucose levels at different time points after i.p injection of human insulin (0.75 U/kg of body weight). (I) AUC was calculated using the trapezoidal rule. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 7–8 per group; # p < 0.05 compared with CD-fed WT mice; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with HFD-fed WT mice.