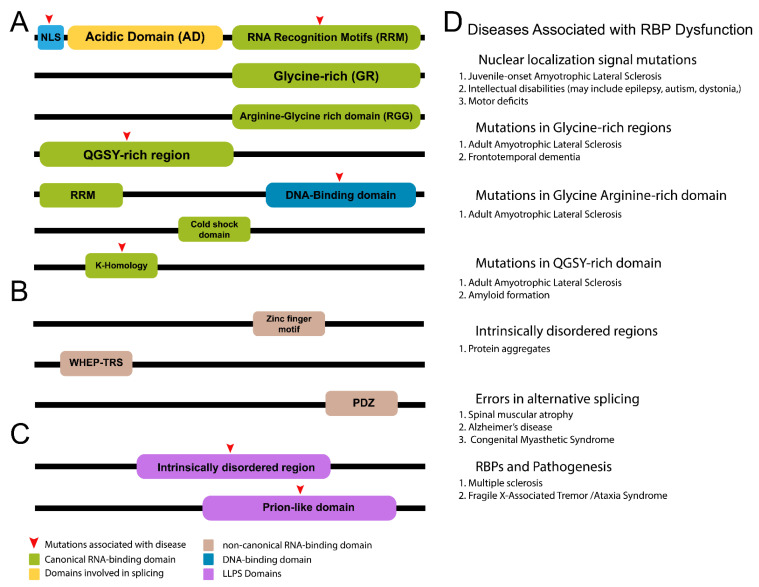
Figure 2.
Structural Properties of RNA-binding proteins. Illustration depicts common RBP domains. (A) Most RBPs contain common RNA-binding domains, such as RRMs, GRs, and QGSY regions. Nuclear localization signals and acidic domains [247] (splicing factors) are also found in various RBPs. (B) Some RBPs contain noncanonical domains that can bind RNA/DNA [184], such as Zn-finger motifs, WHEP-TRS domains [248], and PDZ domains. (C) Other RBPs contain important regions involved in liquid–liquid phase separation that promote formation of biological condensates important for RBP function, such as stress granule formation and transcription. (D) List of RBP domains associated with disease and dysfunction. Common diseases and abnormalities are included [249,250,251,252,253,254].