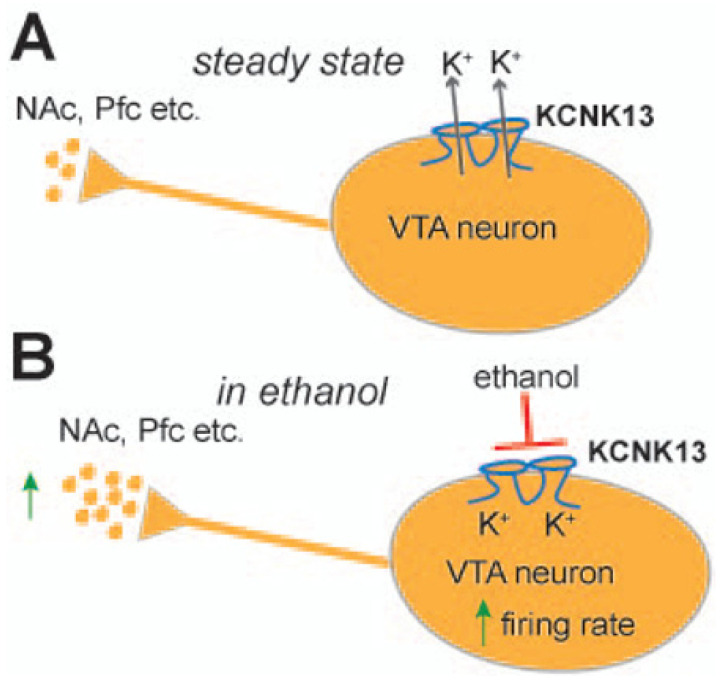
Figure 1.
A schematic showing the steady state of VTA neurons (A) and how acute administration of ethanol stimulates VTA neurons by inhibiting KCNK13 (B); this molecule can modulate both VTA neuronal activity and binge drinking. KCNK13 is expressed in dopamine and non-dopamine neurons in the VTA. Kcnk13 gene expression is upregulated by acute alcohol consumption (Reproduced with permission from [26]).