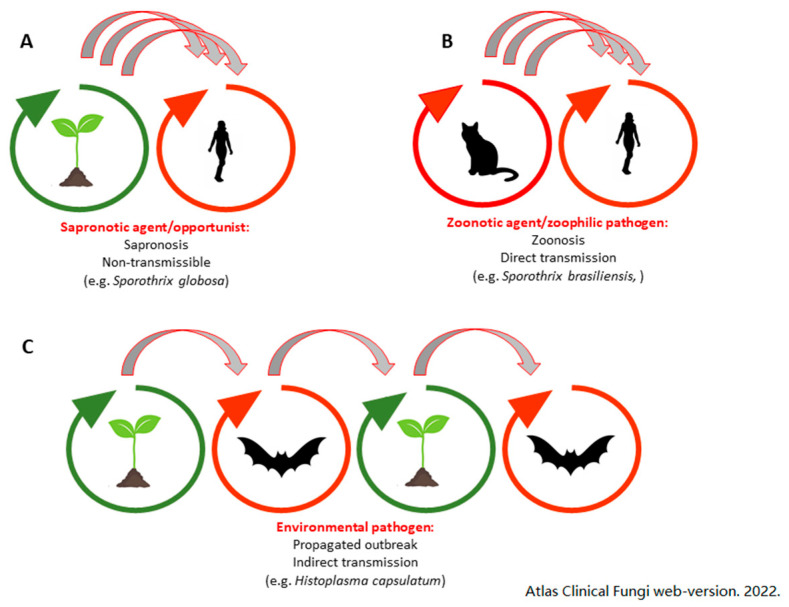
Figure 1.
Lifecycle and mode of transmission of zoonotic agent, sapronotic agent and environmental pathogen. (A) sapronotic agents/opportunists are non-transmissible; outbreak occurs following repeated infection from a common environmental source leading to sapronosis; (B) zoonotic agents/zoophilic pathogens depend on the host for feeding and transmission, which mainly occurs directly via contagious animal hosts; (C) environmental pathogen, feeding and sexuality is environmental, propagation via host, non-contagious. In (A,B), repeated events of transmission occur from the same host/environment as opposed to (C), where a single host is infected and spreads the infective agent in an environment; this is represented by the number of arrows connecting each host and environment. Adapted with permission from ref. [29]. Copyright 2022 Atlas Clinical Fungi web-version.