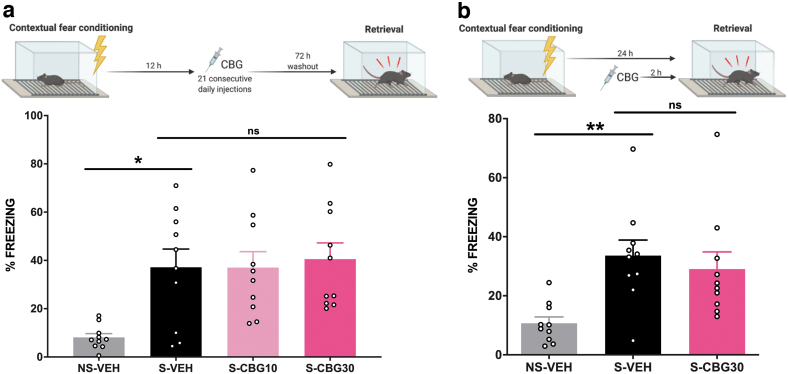
FIG. 1.
CBG did not disrupt long-term conditioned fear memory or conditioned fear memory expression. (a) Long-term fear memory: fear conditioned mice were shocked and 12 h later administered vehicle, or 10 or 30 mg/kg of CBG. Twenty-four hours after the first injection, mice were administered vehicle or CBG, daily for 20 consecutive days. After a 72-h washout, mice were returned to the fear conditioned context and freezing was measured. (b) Fear memory expression: fear conditioned mice were shocked and 2 h before being returned to the fear conditioned context, mice were administered with vehicle or 30 mg/kg of CBG. Percent total freezing during retrieval session was measured. Data are expressed as mean+SEM (n=10 per group). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and indicates significant differences when compared to the NS-VEH group (Mann–Whitney U test). ns, not significant compared to S-VEH (one-way ANOVA or unpaired t-test). NS-VEH, non-shock-vehicle; S-VEH, shock-vehicle; S-CBG10, shock-cannabigerol 10 mg/kg; S-CBG30, shock-cannabigerol 30 mg/kg. ANOVA, analysis of variance; SEM, standard error of the mean.