Figure 1.
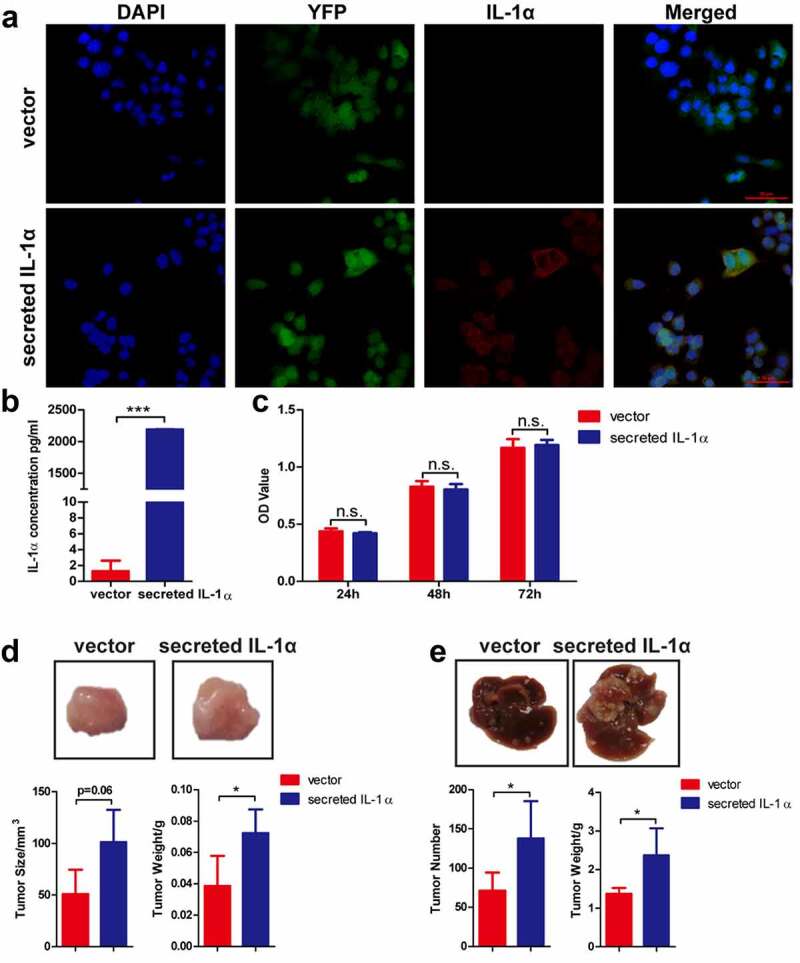
Tumoral-secreted IL-1α promotes tumor growth in murine HCC models.
(a) Immunofluorescence staining detection of the expression of IL-1α (red) in hepa1-6 transfected cells (green). Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue color). Scale bar: 50 µm. (b) The secretion of IL-1α in supernatant of hepa1-6 transfected cells was determined by ELISA assay. (c) The cell proliferation ability was determined by CCK-8 assay. (d) Mice (n = 5 each group) were injected subcutaneously with hepa1-6-secreted IL-1α or -vector cells. The representative of tumor morphology, tumor sizes and tumor weight are shown. (e) Mice (n = 5–7 each group) were injected with hepa1-6-secreted IL-1α or -vector cells via hydrodynamic cell delivery method. Mice were sacrificed 3 weeks later. The representative of tumor morphology, the numbers of tumor nodules and liver weight were shown. The data shown are representative of three experiments. Data are presented as means ± SD. * p < .05, ***p < .001.
