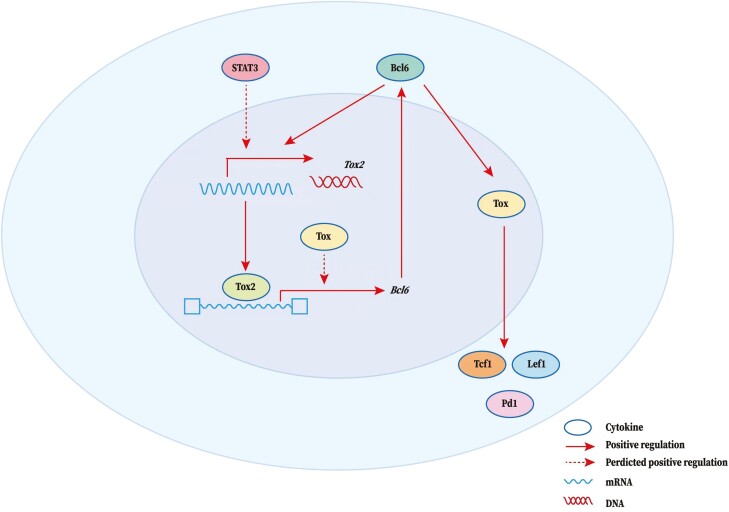
Figure 3:
TOX-related regulatory network in Tfh cell development. TOX functions as a key transcription regulator in Tfh cells. The arrow represents a positive (stimulatory) connection. The solid line represents a link based on genetic evidence, mostly whether this linkage is through direct or indirect binding of transcription factors to target genes remains to be determined. A dashed line indicates an association inferred from the literature, but where genetic support is absent or indirect. BCL6 can promote TOX expression to further promote the expression of multiple molecules including TCF1, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1), and PD-1 which play critical roles in Tfh cell differentiation and function. In addition, Tox2 is highly expressed in Tfh cells and regulated by Bcl6 and STAT3. Tox2 directly binds to Tfh-associated genes (especially BCL6), promoting chromatin accessibility, to further promote the expression of these genes. TOX may also play a facilitating role in this process. Thus, the TOX2-BCL6 axis constructs a transcriptional feed-forward loop that facilitates the Tfh program combined with downstream TOX signaling.