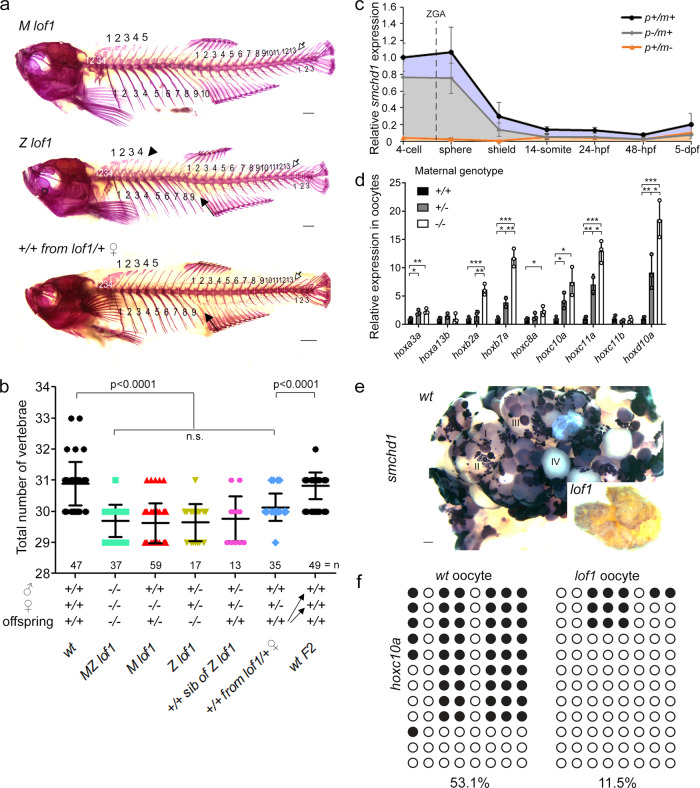
Fig. 3. Skeletal phenotype is caused by maternal Smchd1 haploinsufficiency.
a, b Skeletal preparations of fish of different genotypes. Phenotypes include loss of a rib (filled arrow), loss of a supraneural vertebra (arrowhead) and loss of a caudal vertebra (open arrow) Scale bar = 1 mm. P values were calculated by the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s Multiple Comparison Test. c qPCR shows that there is little to no zygotic smchd1 expression. p: paternal allele; m: maternal allele. n = 3 biological samples. d qPCR shows that hox derepression is already observed in unfertilized oocytes and that oocytes from ± females show intermediate level of hox mis-expression. n = 3 biological samples, p values were calculated by 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. All data are presented as mean values ± SD. e In situ hybridization of smchd1 shows that smchd1 is expressed in developing oocytes. Roman numerals denote stages of oocyte development. Scale bar = 200 µm. f Bisulfite sequencing in oocytes shows hypomethylation of hoxc10a locus when smchd1 is knocked out.