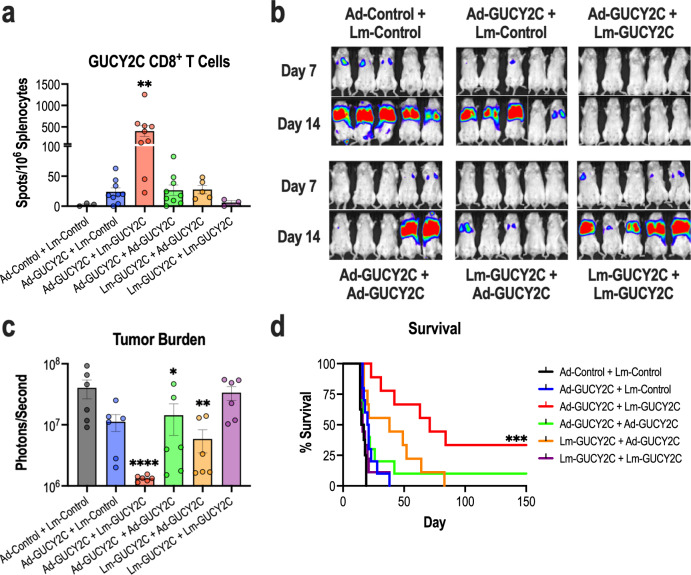
Fig. 2. Heterologous Ad5.F35+Lm immunization enhances GUCY2C-specific CD8+ T-cell responses and antitumor immunity.
a–d BALB/cJ mice (n = 3–9/group) were immunized with a ‘priming’ immunization on day 0 and a ‘boosting’ immunization on day 21 utilizing homologous or heterologous combinations of GUCY2C-expressing and control vaccines. GUCY2C or control adenovirus vaccines were administered intramuscularly (i.m.) at 1010 vp and GUCY2C or control Lm vaccines were administered intravenously (i.v.) at 5 × 106 CFU. Six days after the final immunization, spleens were collected and splenocytes were stimulated with GUCY2C254-262 peptide to quantify GUCY2C-specific CD8+ T cells by IFNγ ELISpot (a) or mice were challenged i.v. with 5 × 105 CT26 colorectal cancer cells expressing GUCY2C and firefly luciferase (b–d). b On days 7 and 14 post-tumor challenge, mice were injected with D-luciferin substrate and imaged. c Day 7 tumor burden was quantified by imaging. d Survival was monitored throughout the experiment. GUCY2C-specific CD8+ T-cell counts (a) and tumor-burden (c) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA compared to control immunization with Dunnett’s test to correct for multiple comparisons. Survival was analyzed by the Mantel-Cox log-rank test with all immunized groups compared to control immunization using the Bonferroni method to correct for multiple comparisons (d). Error bars indicate mean +/− SEM.