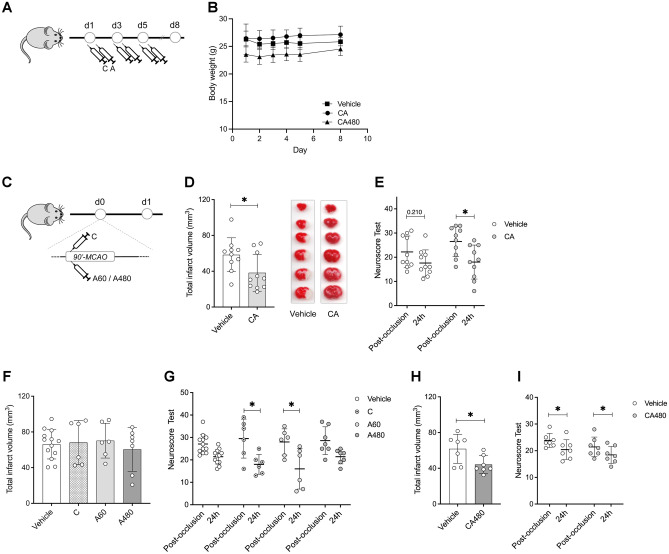
Fig. 2.
Administration of CA showed neuroprotection after stroke. A Experimental design of the safety study. B Body weight monitoring of animals treated with vehicle or ceruletide 0.1 mg/kg and alpha-1 antitrypsin at a dose of 60 mg/kg (CA60) or 480 mg/kg (CA480). C Experimental design of the efficacy study. D Infarct volumes (mm3) of animals treated with vehicle (n = 10) or ceruletide (0.1 mg/kg) + alpha-1 antitrypsin (60 mg/kg) (CA, n = 10) 24 h after cerebral ischemia. E Neurological deficits of animals evaluated post-occlusion (80 min after MCAO induction) and 24 h after the ischemic event. F Infarct volumes (mm3) of animals treated with vehicle (n = 10) or single drugs (n = 6 for ceruletide (C), n = 6 for alpha-1 antitrypsin at a dose of 60 mg/kg (A60) and n = 7 for alpha-1 antitrypsin at 480 mg/kg (A480)). G Neurological deficits of animals evaluated post-occlusion and 24 h after the ischemic event. H Infarct volumes (mm3) of animals treated with vehicle (n = 10) or ceruletide (0.1 mg/kg) + alpha-1 antitrypsin (480 mg/kg) (CA480, n = 10) 24 h after cerebral ischemia. I Neurological deficits of animals evaluated post-occlusion and 24 h after the ischemic event. In all cases, mean ± SD is shown. * indicates p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01