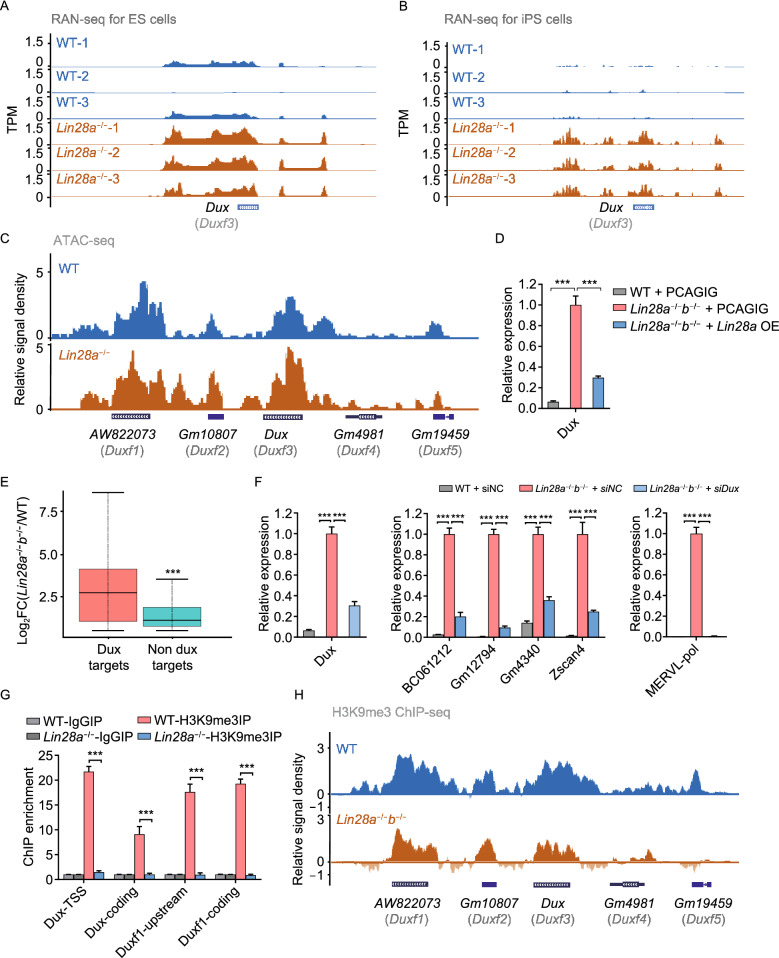
Figure 3.
LIN28 regulates ERV expression through repression of Dux. (A and B) UCSC Genome Browser view showing RNA-seq results at Dux gene in the indicated ES cells (A) or iPS cells (B). (C) ATAC-seq tracks at the Dux family loci in wide-type (blue) and Lin28a knockout (brown) ES cells. (D) qRT-PCR showing Dux gene expression in wild-type and double knockout iPS cells transduced with empty vector or Lin28a overexpressing vector (relative expression normalized to Gapdh). (E) Boxplot showing that Dux targets are significantly more induced than non-targets by analyzing the upregulated genes in Lin28 double knockout iPS cells. (F) qRT-PCR showing Dux, 2C gene and MERVL expression in wild-type and Lin28 double knockout iPS cells treated with scramble negative control or the Dux siRNAs. (G) ChIP-qPCR showing H3K9me3 levels for Dux gene locus in wild-type and knockout ES cells. IgG was used as control. (H) UCSC Genome Browser view of H3K9me3 ChIP-seq results for the Dux family. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA, n = 3, error bar: standard error of the mean