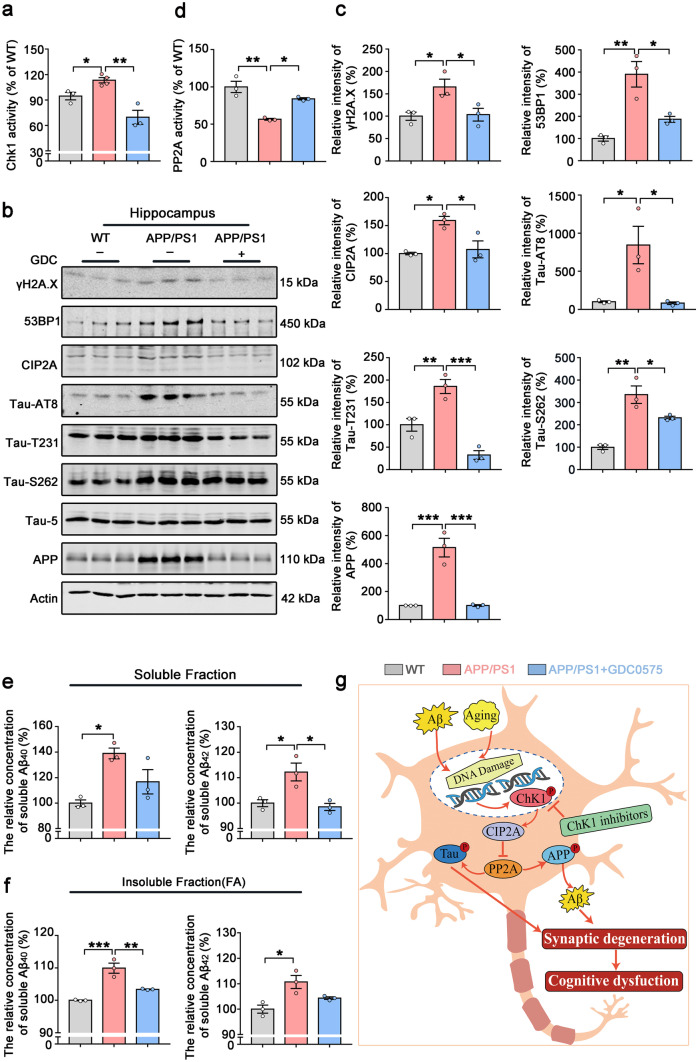
Fig. 8.
Chk1 inhibitor (GDC-0575) ameliorates CIP2A upregulation, tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ production in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. a Chk1 activity was detected in the hippocampus of the mice. b Representative immunoblots of γH2A.X, 53BP1, CIP2A, Tau-AT8, Tau-T231, Tau-S262, Tau-5, APP, and β-actin in the hippocampus of the mice. Blots were from different gels with the same batch of samples electrophoresed. c The quantitative analysis of the protein level in b. Non-phosphorylated proteins such as γH2A.X, 53BP1, CIP2A, and APP were normalized to the β-actin levels; phosphorylated Tau-S262, Tau-AT8, and Tau-T231 were normalized to total tau (Tau-5) levels. d PP2A activity was detected in the hippocampus of the mice. e The soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 in the mice hippocampal tissues were detected by ELISA kit. f The insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 in the mice hippocampal tissues were detected by ELISA kit. All data represent mean ± SEM, a APP/PS1 group n = 4, b–f n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, comparison between the two groups. g Summary of the role of Chk1 activation in promoting AD-like pathologies through CIP2A/PP2A signaling