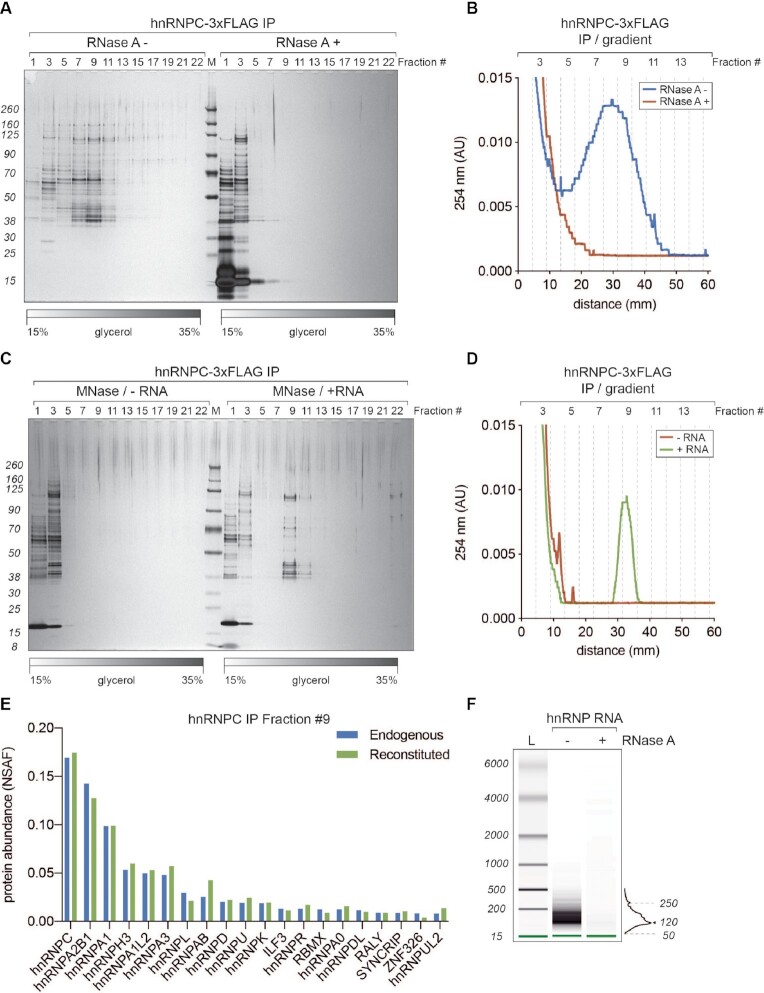
Figure 3.
40S hnRNP particles are dynamic, RNA-dependent assemblies. (A) SDS-PAGE/silver staining analysis of 15–35% glycerol gradient fractions from hnRNP C-3xFLAG purifications without (RNase A–) and with (RNase A+) treatment after the elution. (B) UV A254 nm profile of two gradients displayed in A. Blue trace corresponds to RNase A– and red to RNase A+ condition, respectively. (C) SDS-PAGE/silver staining analysis of 15–35% glycerol gradient fractions from hnRNP C-3xFLAG purifications where eluates were treated with micrococcal nuclease (MNase) to remove associated RNA. Before loading on a gradient, MNase-digested samples were either incubated with an in vitro transcribed fragment of HBB pre-mRNA (+ RNA) or loaded directly (–RNA). (D) UV A254 nm profile of the gradients displayed in (C). Green trace corresponds to +RNA and red to –RNA condition, respectively. (E) MS analysis of fractions 9 from gradients displayed in C (+RNA) and 2B (hnRNP C-3xFLAG IP). Plotted are top 20 the most abundant proteins from both purifications (hnRNP C-3xFLAG in blue and reconstituted in green, respectively). Hits are sorted based on their NSAF (normalized spectral abundance factor) values. (F) RNA length analysis (BioAnalyzer system) of samples extracted from gradient hnRNP fractions displayed in (A).