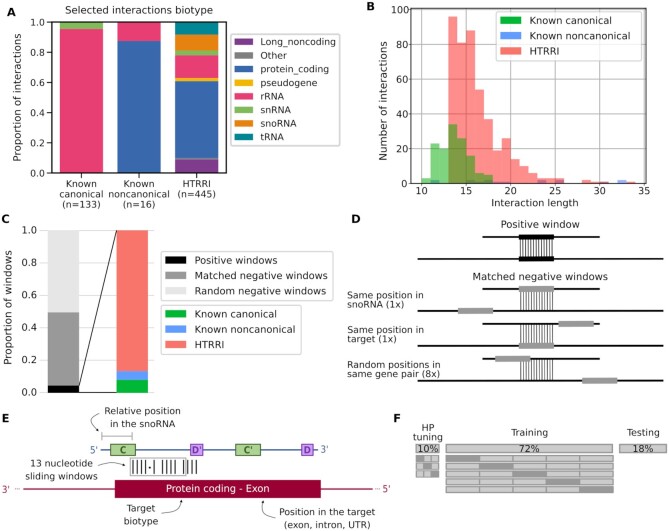
Figure 2.
Composition of the dataset used to build snoGloBe. (A) Diverse RNAs have been shown to bind box C/D snoRNAs. Interactions involving box C/D snoRNAs were collected and assembled including known canonical interactions with rRNA and snRNA from snoRNABase, known noncanonical interactions curated from the literature and interactions extracted from HTRRI datasets. The proportion of interactions involving different RNAs of each biotype is shown for each interaction source. The color legend for RNA biotypes is shown on the right. (B) Distribution of the length of interactions from each data source. (C) Distribution of the datasets used to build snoGloBe. The dataset consists of positive, matched negatives and random negatives in a proportion of 21 negatives (10 matched and 11 random) for 1 positive window. The positive windows are composed of HTRRI (86.3%), known canonical (8.5%) and noncanonical (5.2%) interactions. (D) Generation of matched negative windows. 10 matched negative windows are generated for each positive one. The matched negative windows originate from the same snoRNA–target gene pair as the positive window. One has the same position in the snoRNA and a different position in the same target, one has a different position in the snoRNA and the same position in the target, and 8 windows have random positions in the same snoRNA–target pair. (E) SnoRNA–RNA pairs are encoded for presentation to the predictor. Features considered include the 13 nucleotide sequence of the snoRNA and the 13 nucleotide sequence of the target, the relative position of the window in the snoRNA, the target biotype and the position in the target. (F) The dataset is split in non-overlapping sets for hyperparameter tuning (10% of the windows), training (72% of the windows) and testing (18% of the windows). The hyperparameter tuning was done using a random search with 3-fold cross-validation. The model was trained and evaluated using stratified 5-fold cross-validation to ensure the correct representation of each category of positive windows in each subset. The known noncanonical windows were all kept for the validation set.