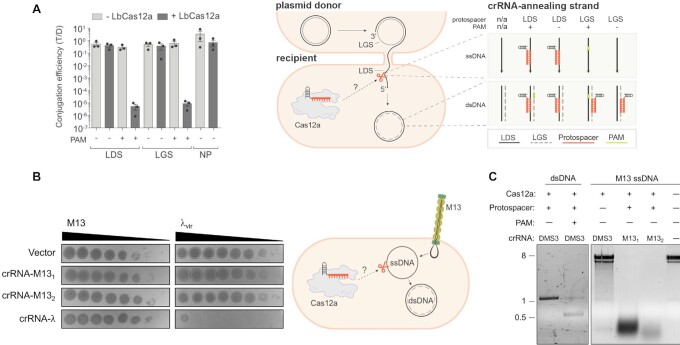
Figure 2.
Cas12a does not detectably cis-cleave invasive ssDNA in bacteria. (A) Conjugation efficiency for plasmid cis-targeting in P. aeruginosa PAO1 strain. During conjugation, the donor is nicked and the leading strand (LDS) is transferred as ssDNA to the wildtype (-LbCas12a) or LbCas12a-expressing (+LbCas12a) recipient cell via the mating pilus. LbCas12a was co-expressed with crRNAs complementary to a DMS3 protospacer cloned into the leading (LDS) or lagging (LGS) strand, with (+) or without (–) the correct protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). T/D indicates the ratio of transconjugants to donors. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). LDS, complementary protospacer is on leading strand; LGS, complementary protospacer is on lagging strand; NP, no protospacer on plasmid. (B) Plaque assay for phage cis-targeting in E. coli BW25113 F’ strain. Bacterial lawns were infected with dsDNA λvir or with M13, which enters and leaves the cell as ssDNA but replicates via a dsDNA intermediate. LbCas12a was co-expressed in bacteria with crRNA complementary to M13 positive strand (without PAM) or λvir (with PAM) during phage infection. Bacterial clearance (black) indicates phage replication. (C) In vitro LbCas12a cleavage assay on dsDNA template encoding DMS3 protospacer or M13 ssDNA.