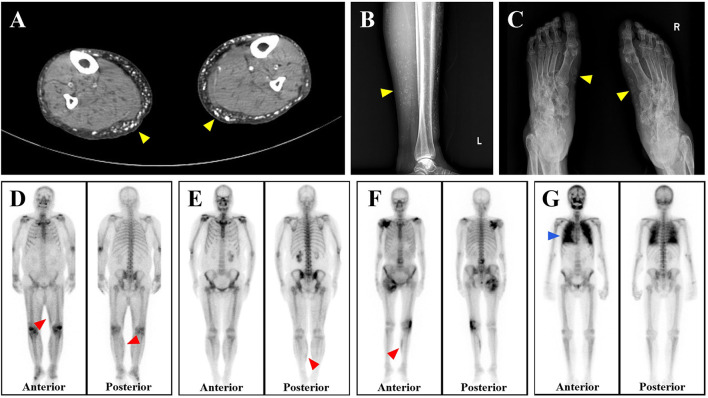
Figure 3.
Imaging characteristics of calciphylaxis. (A–C) Both CT and X-ray reveal subcutaneous extravascular diffuse calcium deposition of patients with calciphylaxis (yellow arrows, shown as white). (D–F) Bone scintigraphy shows the increased uptake of radiotracer by subcutaneous soft tissues of three calciphylaxis patients, especially the continuous linear abnormal radioactive concentration in the lower limbs (red arrows, shown as black). (G) Diffuse uptake enhancement is also observed with bone scintigraphy when calciphylaxis involves internal organs such as the lungs (blue arrows).