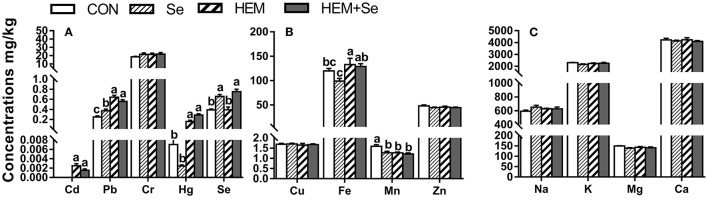
Figure 1.
The effect of selenium and cadmium, lead, mercury, and chromium Co-treatment on the concentrations of ions in the egg yolk (Wet Basis mg/kg) of laying hens from 63 to 74 wk of age. CON, corn-soybean meal basal dietary; Se, the basal dietary supplemented with 0.4 mg/kg selenium from selenized yeast (the selenium concentration was 0.14 mg/kg in the CON diet); HEM, the basal dietary supplemented with 5 mg/kg cadmium from CdCl2, 50 mg/kg lead from Pb(NO3)2, 3 mg/kg mercury from HgCl2 and 5 mg/kg chromium from CrCl3; HEM+Se, the HEM dietary supplemented with 0.4 mg/kg selenium from selenized yeast. (A) The effect of selenium and cadmium, lead, mercury, and chromium Co-treatment on the concentrations of cadmium, lead, chromium, mercury, and selenium in the egg yolk. (B) The effect of selenium and cadmium, lead, mercury, and chromium Co-treatment on the concentrations of copper, iron, manganese, and zinc in the egg yolk. (C) The effect of selenium and cadmium, lead, mercury, and chromium Co-treatment on the concentrations of sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium in the egg yolk. a,b,c Bars without a shared common letter are significantly different (p < 0.05). Data show the mean ± SEM (n = 10).