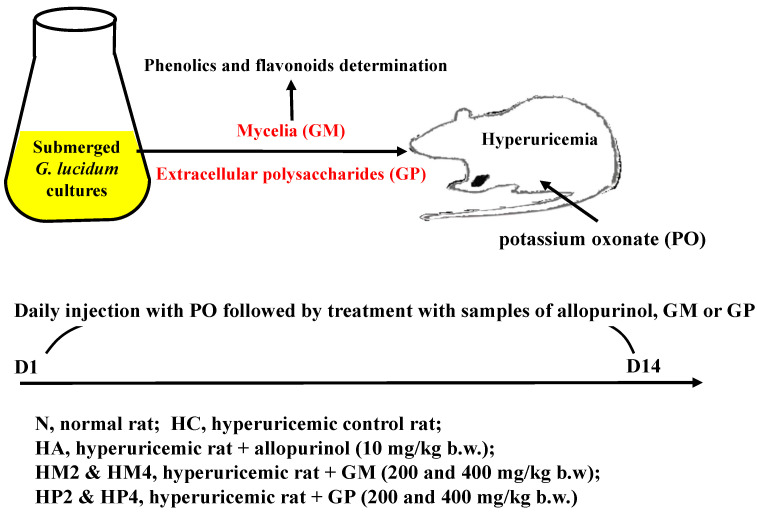
Figure 5.
Protocol of hyperuricemia induction and treatment of rats. Sprague-Dawley rats were intraperitoneal injected with potassium oxonate (PO; 250 mg/kg b.w.) daily to induce hyperuricemia. The rats in the normal (N) group did not receive any treatment throughout the animal experiment. PO-injected rats were randomly divided to 6 groups (n = 8): hyperuricemic control (HC), daily treated with allopurinol (10 mg/kg b.w.; HA), daily treated with GM (200 or 400 mg/kg b.w.; HM2 or HM4), or daily treated with GP (200 or 400 mg/kg b.w.; HP2 or HP4). Except for the rats in N and HC groups, the other rats were orally treated with allopurinol or G. lucidum formula daily. The rats were treated for 2 weeks and then sacrificed on day 15 to individually isolate and weigh the kidney and liver. The blood samples, as well as liver samples, were harvested for further analysis.