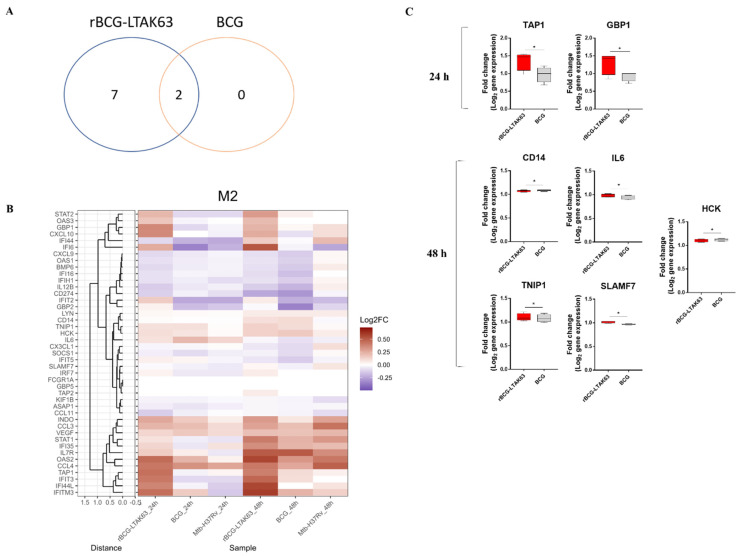
Figure 2.
BCG infection downregulates an inflammatory gene profile in M2 macrophages 48 h post-infection, while rBCG-LTAK63 infection maintains or further upregulates genes associated with inflammation. M2 macrophages derived from 4 different donors were infected with rBCG-LTAK63, BCG, or Mtb H37Rv, and transcriptomic profiles were determined at 24 h and 48 h post-infection by dcRT-MLPA. (A) Venn diagram displaying the number of differentially expressed genes (p ˂ 0.05) identified in rBCG-LTAK63- or BCG-infected M2 macrophages at 48 h (fold change in relation to uninfected M2 macrophages). (B) Heat map showing fold changes in expression profile of the 43 immune-related genes in M2 macrophages in response to infection with rBCG-LTAK63, BCG, or Mtb H37Rv for 24 h or 48 h. (C) Differentially expressed genes (p ˂ 0.05) in rBCG-LTAK63-infected M2 macrophages compared to BCG-infected M2 macrophages. Statistical significance was determined by paired Student t-test. Significant differences were observed as indicated * p ˂ 0.05.