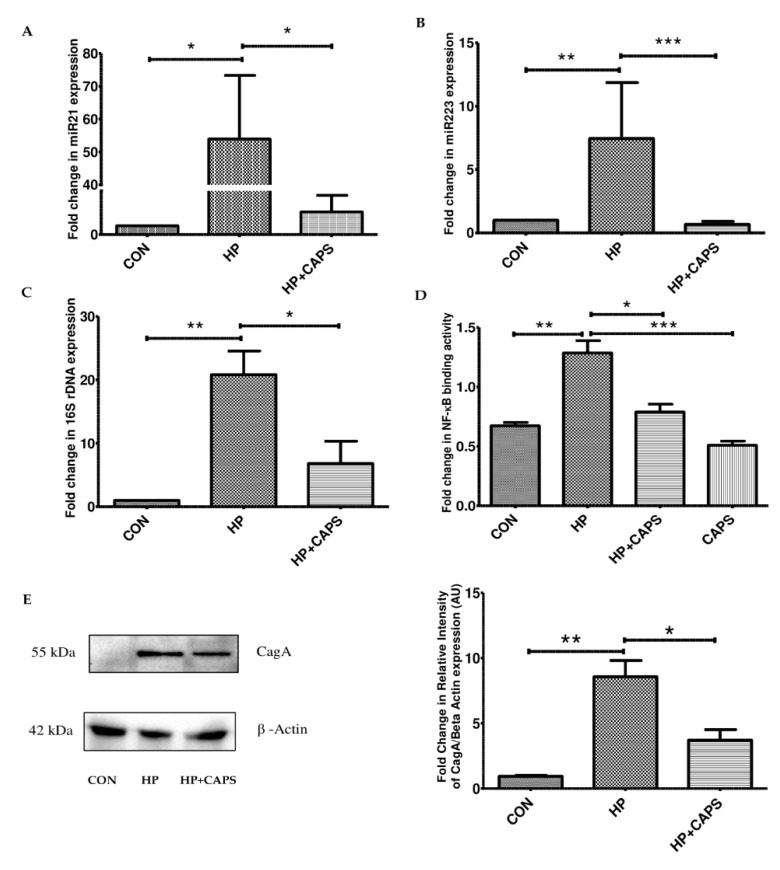
Figure 3.
Capsaicin reduces NF-kB-regulated miRNA expression and H. pylori infection. (A,B) Real-time PCR showing the expression levels of miR21 and mir223 in capsaicin-treated mice samples as compared to H. pylori infected samples. In case of miRNAs, U6 was used as control to normalize miRNAs. Control (CON), H. pylori infected (HP), H. pylori infected + Capsaicin treated (HP + Caps). (C) Real-time PCR was performed to detect H. pylori specific 16s ribosomal DNA. (D) Control (CON), H. pylori infected (HP), H. pylori infected + Capsaicin treated (HP + Caps) and only Capsaicin (CAPS) treated AGS cells were subjected to NF-kB promoter assay. Promoter assay was performed to show the activation of NF-kB binding to the promoter sequence. (E) Western blot showing H. pylori infection increased expression of virulence factor CagA, while capsaicin treatment (100 μM) decreased it significantly in AGS cell line. β actin was used as loading control. Densitometry of representative blot was performed, and values are tested by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. ‘*’, ‘**’ and ‘***’ represent significant differences between groups at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, respectively.