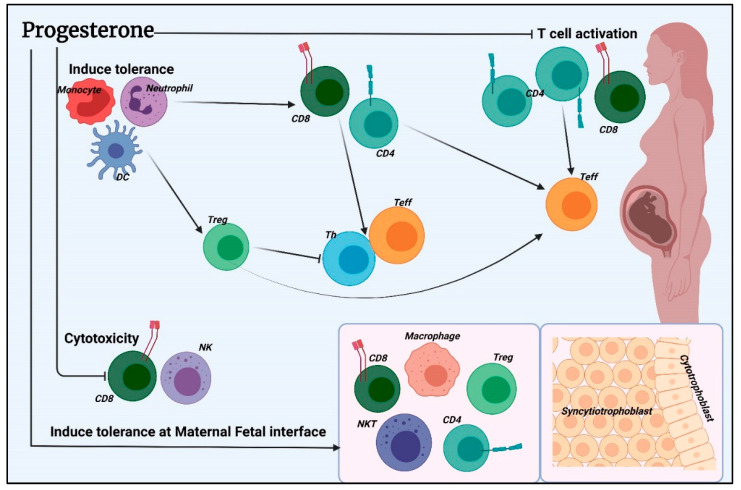
Figure 1.
Summary of progesterone immunomodulatory mechanism. P4 directly influences T cell activation and differentiation by modulating TCR signal transduction or indirectly by generating tolerant antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells (DC) that inhibit T cell activation during TCR interaction. P4 can also inhibit cellular cytotoxicity. P4 can promote placental tissue growth and invasion at the maternal-fetal interface by inducing immune-tolerant phenotypes of macrophages, natural killer (NK), and T regulatory (Treg) cells, as well as exhausting activated CD4 and CD8 T cells that have interacted with placental-derived fetal-paternal antigens. Chemoattractant molecules produced on placental tissue help these tolerant leukocytes migrate to maternal-fetal contact. Created with BioRender.com.