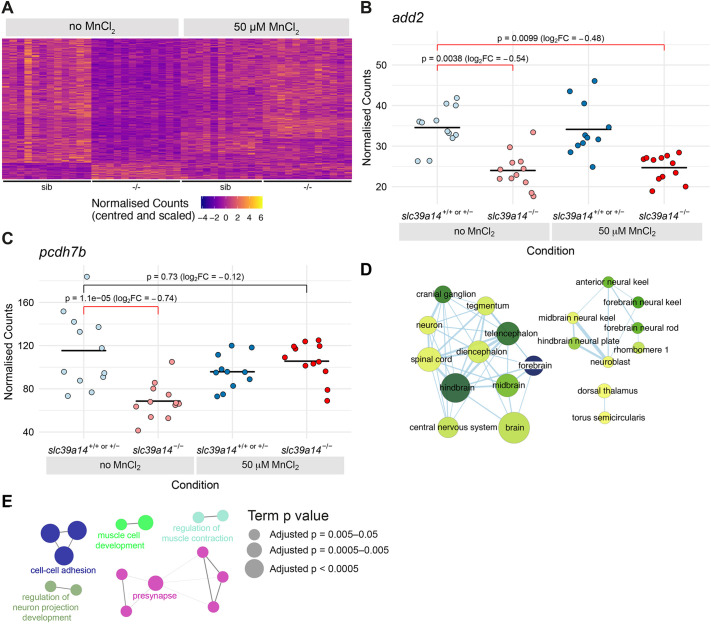
Fig. 7.
Exogenous Mn restores normal expression of genes that are differentially expressed in unexposed slc39a14−/− mutants. (A) Heatmap of the expression of 266 genes with a significant difference between unexposed mutants and unexposed siblings. Each row represents a different gene and each column is a sample. The normalised counts for each gene have been mean centred and scaled by dividing by the standard deviation. (B) Plot of normalised counts for the add2 gene. Gene expression is decreased in both unexposed and MnCl2-exposed mutant embryos. Unexposed sibling embryos are indicated in light blue and Mn-exposed embryos are in dark blue. Unexposed mutants are coloured light red and exposed mutants are dark red. (C) Plot of normalised counts for the pcdh7b gene. There were decreased counts in the unexposed mutant embryos that were rescued back to wild-type levels upon 50 µM MnCl2 treatment. Colour scheme is as in B. FC, fold change. Wald test was used to determine significance in B,C. (D) Enrichment Map diagram of the enrichment of ZFA terms for the genes differentially expressed in unexposed mutants that are rescued by Mn treatment. Nodes represent enriched ZFA terms and edges connect nodes that share annotations to the significant genes. The width of each edge is proportional to amount of overlap, nodes are coloured by −log10[adjusted P-value] (Wald test) and the size represents the number of significant genes annotated to the term. (E) ClueGO network diagram of the enrichment of GO terms associated with the genes that are rescued by Mn treatment. Nodes represent enriched GO terms and edges connect nodes that share annotations to the significant genes. Different components of the network are coloured according to the categories as labelled on the diagram. The sizes of the circles represent the adjusted P-values for each GO term as indicated on the right (Wald test).