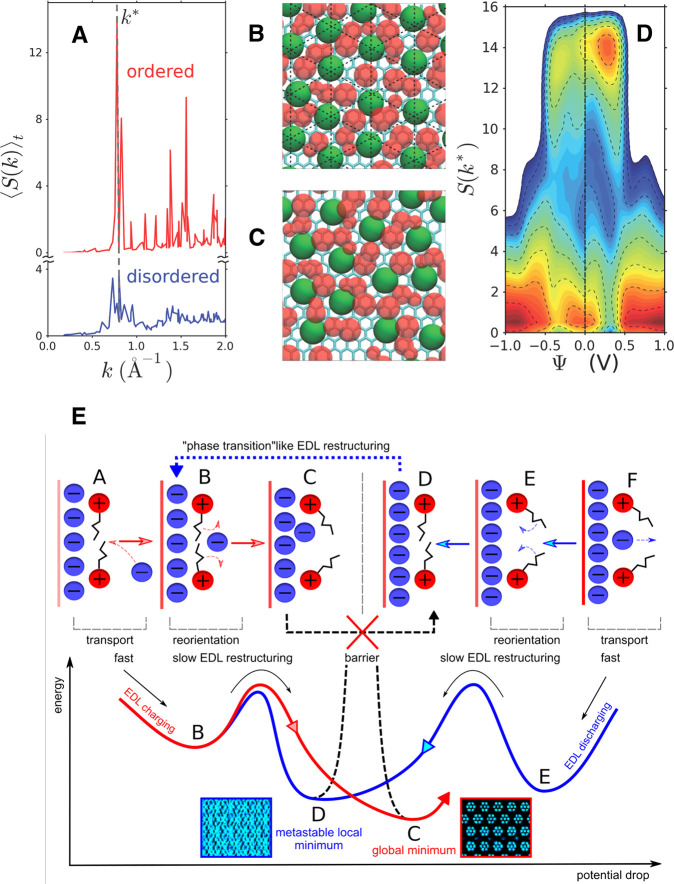
Figure 8.
Two-dimensional structural transitions at the surface of planar electrodes. (A) Average anion–anion structure factor in the first adsorbed layer of BMIM-PF6 ionic liquid adsorbed on graphite electrodes, as a function of the norm of the in-plane wave vector, for a null applied voltage. (B) Representative snapshot of the adsorbed layer in the ordered phase (a coarse-grained model is used; green spheres, (PF6–) anions; red spheres, (BMIM+) cations). (C) Representative snapshot of the adsorbed layer in the disordered state. (D) Probability distribution of the anion–anion structure factor at the maximum S(k*) in the first adsorbed layer on the electrodes, as a function of the electrode voltage. The probability is reported on a logarithmic scale, with lines separated by a difference of 0.5. Three distinct basins emerge from the analysis. Reproduced with permission from ref (162). Copyright 2014 American Chemical Society. (E) Schematic overview of the anion and cation reorganizations within the adsorbed layer during the surface discharging/charging. The energy diagram shows the activation barriers involved during these processes. Reproduced with permission from ref (203). Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society.