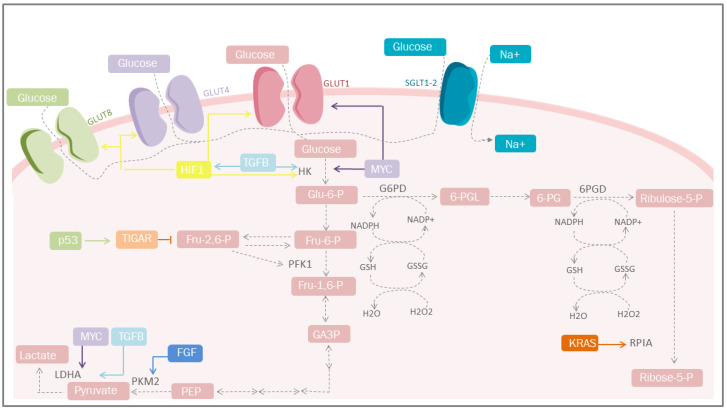
Figure 1.
Carbohydrate metabolism and mediators of metabolic reprogramming. Cancer cells must acquire a greater amount of nutrients, especially glucose. One of the mediators is HIF-1, which increases glucose uptake through the induction of GLUT-1, GLUT-4 and GLUT-1; simultaneosly, it can also be stimulated by TGF-β through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Other important mediators are p53 that plays a protective role against ROS. GLUT, glucose transporters; Glu-6-P, glucose 6-phosphate; Fru-6-P, fructose 6-bisphosphate; Fru-1,6-P, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; Fru-2,6-P, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate; GA-3-P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; HK, hexokinase; TGFB, transforming growth factor beta; PFK1, phosphofructokinase 1; PKM2, pyruvate kinase M2; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; 6-PGL, 6-phosphogluconolactonase; NADP+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, reduced form of NADP; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; GSH, glutathione; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; TIGAR, Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; KRAS, Kirsten-ras; RPIA, ribose-5 phosphate isomerase; MYC, proto-oncogene; Ribulose-5-P, ribulose 5-phosphate; Ribose-5-P, ribose 5-phosphate; SGLT1/2, sodium-glucose cotransporter-1/2.