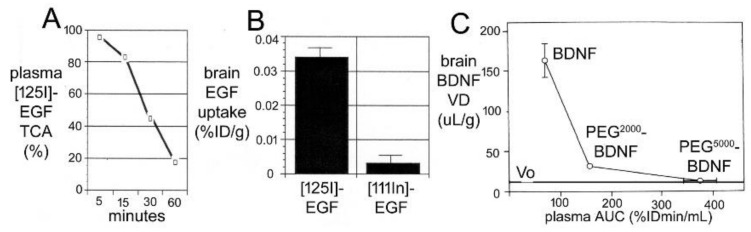
Figure 22.
Peptide metabolism and artifacts of brain uptake of radiolabeled peptide. (A) Rapid a of trichloroacetic acid (TCA)-precipitable plasma radioactivity following the IV injection of [125I]-EGF in the rat. (B) Brain uptake of radioactivity is increased >10-fold following the IV injection of [125I]-EGF as compared to brain uptake after the IV injection of [111In]-EGF. (A,B) drawn from data reported in [805]. (C) The brain/plasma ratio of radioactivity is equal to the brain volume of distribution (VD), and this is plotted against the plasma AUC for 3 forms of radio-iodinated BDNF: [125I]-BDNF, [125I]-PEG2000-BDNF, and [125I]-PEG5000-BDNF. The progressive pegylation of BDNF with PEG2000 and then PEG5000 blocks the peripheral metabolism of BDNF, as reflected in the increasing plasma AUC. As the BDNF metabolism is progressively inhibited, the brain VD of BDNF decreases. The Vo, 13 ± 1 μL/g, shown by the horizontal bar is the brain plasma volume measured with [14C]-rat albumin. The brain VD of BDNF following pegylation with PEG5000 completely suppresses peripheral metabolism of the BDNF and the brain VD = Vo, which shows that BDNF does not cross the BBB. Reproduced with permission from [1139], Copyright© 1997 Springer-Nature.