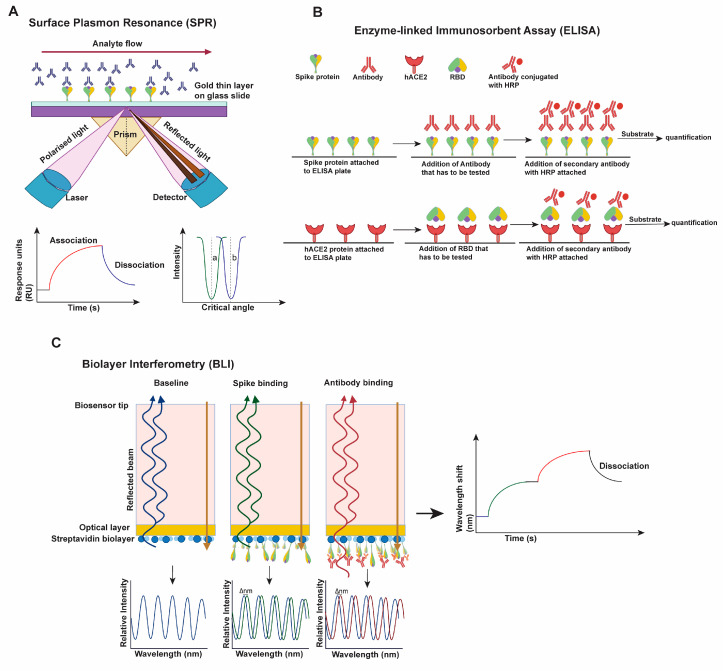
Figure 2.
Schematics depicting the ligand-binding techniques used to characterize the binding of S to antibodies or hACE2. (A) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique. SPR is an optical technique that can be used to analyze the binding of S protein with antibodies or hACE2. One of the interacting molecules is immobilized in the gold-layer sensor chip, and another interacting partner is flown through the microfluidic system. The interaction between the two molecules causes the change in the refractive index of the light, which is recorded as the response signal and measured in the response unit (RU). The plot generated by monitoring RU over time yields the binding kinetics for two interacting molecules. (B) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). ELISA, which is based on the antigen-antibody interaction, effectively profiles the binding of S or its fragment (such as RBD) to an antibody or hACE2. The quantification of binding is evaluated based on the HRP chemiluminescence (conjugated to secondary antibody) or the conjugated fluorescent protein. (C) Bio-layer interferometry (BLI) analysis. BLI is an optical technique for exploring the interaction between S and an antibody or hACE2. One of the interacting molecules is immobilized in the streptavidin layer attached to the biosensor, and another interacting molecule remains in the solution. Binding events of each molecule in the biosensor result in the change in the interference pattern when white light is passed through it. The plot of this change over time yields the binding kinetics of two molecules.