Table 1.
Polymorphs of Gallium Oxide.
| Structure | Comments | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
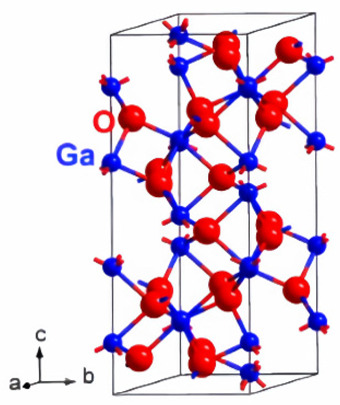
| α-Ga2O3 |
|
This structure is another common structure, apart from beta gallium oxide. It has a similar corundum structure to Al2O3. Making fine crystals is a difficult job. The α-Ga2O3 structure can be maintained only at around 550 °C and above that a phase transformation to β-Ga2O3 takes place. | [18,51,53] |
| β-Ga2O3 |

|
It is the most stable of all in ambient condition and has major interest from researchers and, as already mentioned, it has a monoclinic structure with parameters a = 12.19 A, b = 3.016 A, c = 5.80 A β = 103.70 | [54,55,56] |
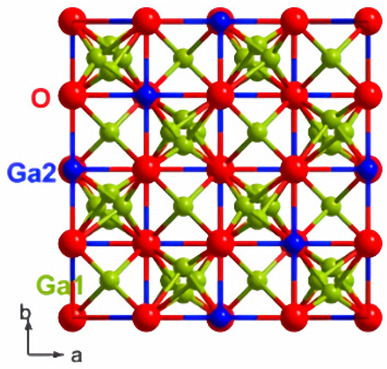
| γ-Ga2O3 |
|
The preparation of this polymorph is simple as it just requires the oxidation of gallium in amino alcohol, like ethanolamine. | [57,58] |
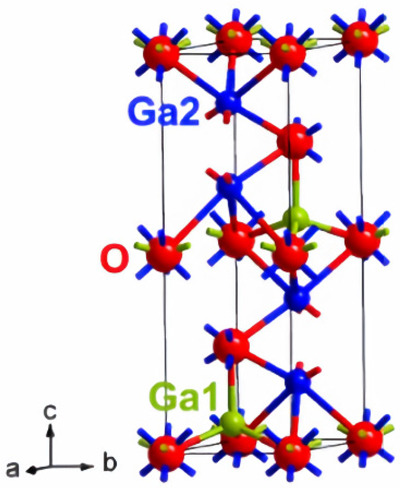
| ε-Ga2O3 |
|
This structure of gallium oxide can be metastable at higher pressure conditions. Also, upon heating it can transform to alpha and beta phases. Furthermore, it exhibits ferroelectric property. |
[59,60] |
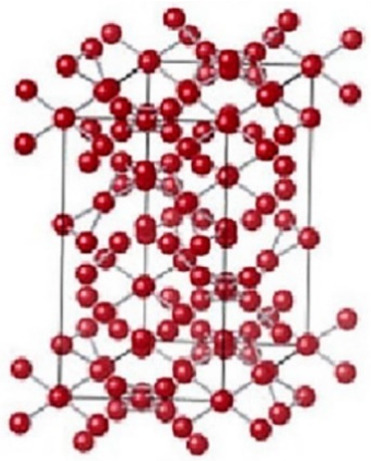
| δ-Ga2O3 |
|
This structure was initially thought to be a phase which was similar to ε-Ga2O3. The structure was presumed to be a nano-crystal form of ε-Ga2O3. However, later it was confirmed that it is not a nanostructure or another phase and is a different cubic structure. | [61,62] |
