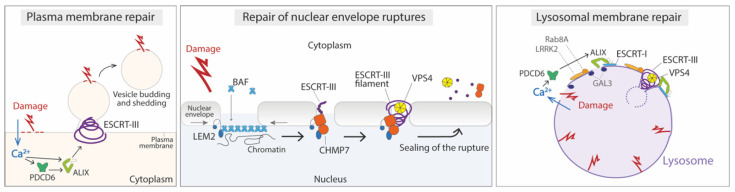
Figure 3.
Membrane repair processes mediated by ESCRT. Left panel: plasma membrane repair. Entry of calcium through the damaged membrane triggers rapid ESCRT recruitment, mediated by PDCD6 and ALIX. ESCRTs are thought to promote membrane budding and shedding of small domains containing the site of damage; middle panel: nuclear envelope (NE) repair. Upon NE rupture, cytosolic BAF coats the exposed chromatin and interacts with LEM2, facilitating the recruitment of nuclear membrane and the interaction with CHMP7. CHMP7 subsequently promotes the nucleation and polymerization of ESCRT-III, which together with VPS4 constricts the rupture and promotes sealing; right panel: lysosome repair. After damage, calcium efflux from the lysosome promotes ESCRT-I and -III recruitment through PDCD6, ALIX, and probably other factors like GAL3 and LRRK2, which phosphorylate the small GTPase Rab8A. It is thought that the membrane-remodeling performed by ESCRT-III filament spirals acts to shed damaged membranes into the lumen of the lysosome for recycling.