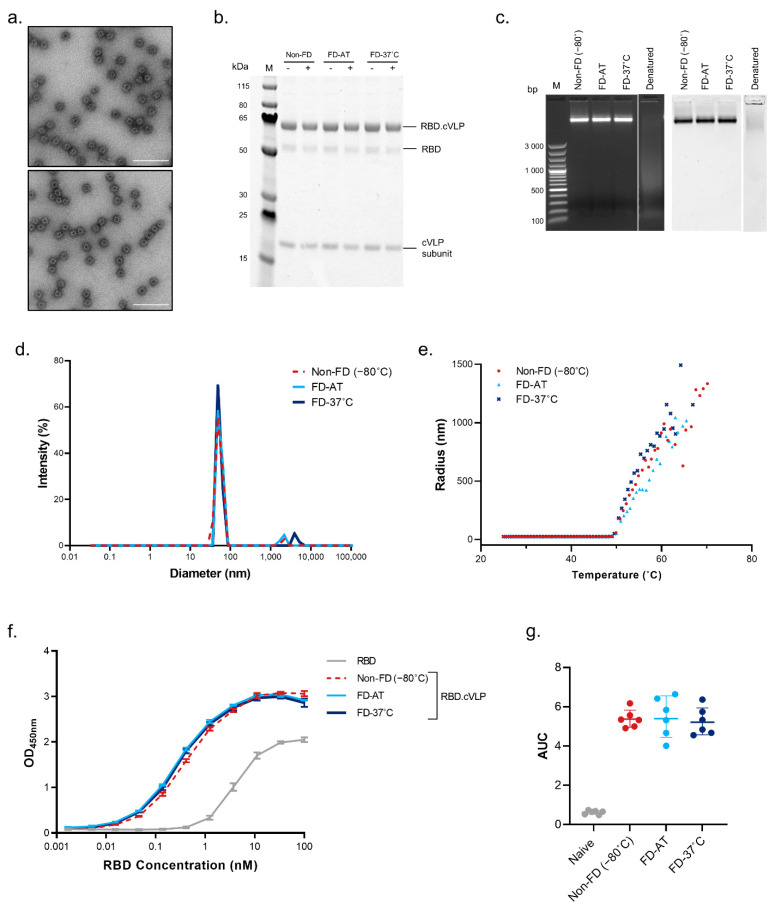
Figure 3.
RBD-cVLP (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine maintains its stability and immunogenicity after freeze-drying. RBD-cVLP vaccine was freeze-dried and stored at ambient temperature (FD-AT) or 37 °C (FD-37 °C) for 1 week (A) or 2 months (B–G). The stability of freeze-dried and reconstituted material was compared to a frozen, non-freeze-dried (non-FD (−80 °C)) reference sample. (A) Negative stain transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of a non-freeze-dried RBD-cVLP reference sample (top panel) and freeze-dried RBD-cVLP (bottom panel). Scale bar represents 200 nm. (B) Representative reduced SDS-PAGE analysis showing non-freeze-dried and freeze-dried RBD-cVLP (stored at ambient temperature or 37 °C) before (-) and after (+) centrifugation. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis stained with ethidium bromide (left) and Coomassie brilliant blue (right). Native non-FD and FD samples were run in parallel to a denatured reference sample. (D) Overlay of DLS analysis of non-FD and FD RBD.cVLP. (E) Thermal stability of freeze-dried RBD.cVLP. DLS was used to measure the hydrodynamic radius of particles at increasing temperatures, from 25 °C to 80 °C. (F) ACE2 receptor binding assay. The binding of unconjugated (soluble) RBD and RBD.cVLP (non-FD and FD) to the human ACE2 receptor was measured in ELISA. Results show the mean ± SD absorbance of the assay run in triplicate. (G) Immunogenicity of freeze-dried RBD-cVLP. Anti-Spike IgG ELISA titers measured in serum samples from mice (n = 6) immunized with either non-FD or FD RBD.cVLP vaccine. Results show the mean ± SD area under the curve (AUC) titer.