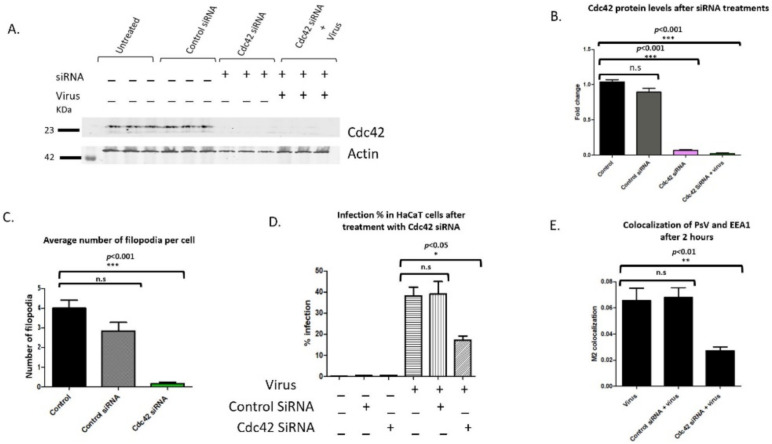
Figure 8.
siRNA mediated knockdown of Cdc42 results in a significant decrease in infection and internalization. Cc42 protein levels were knocked down with siRNA. Cells were treated with control siRNA and Cdc42 siRNA for 48 h. (A) Western blot analysis of siRNA knockdown using Cdc42 and actin antibodies. Cells were incubated with virus on ice for 2 h and unbound virus was washed from wells. Cdc42 protein levels were normalized with actin. (B) Densitometry of western blot showing a significant decrease in Cdc42 protein levels after 48 h even with the addition of virus (samples compared to control with no siRNA or virus, n = 3, ***, p < 0.001). (C). Average number of filopodia per cell after siRNA treatments. Filopodia were counted along the cell periphery with FiloQuant image J plugin, single image analysis. Statistical significance was determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (compared samples to control cells not treated with universal or Cdc42 siRNA, n = 50, ***, p < 0.001). (D) Flow cytometry was performed on cells transfected with control and Cdc42 siRNA. Graph of infection percentages in HaCaT cells treated with control siRNA, Cdc42 siRNA, and virus. Statistical differences were determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (samples compared to control infection, n = 9, *, p < 0.05). (E) Graph representation of colocalization between PsV and EEA1 after 2 h of viral addition for three independent experiments. Statistical difference was determined by unpaired two-tailed t-test (n = 6, **, p < 0.01). Average was displayed with SEM.