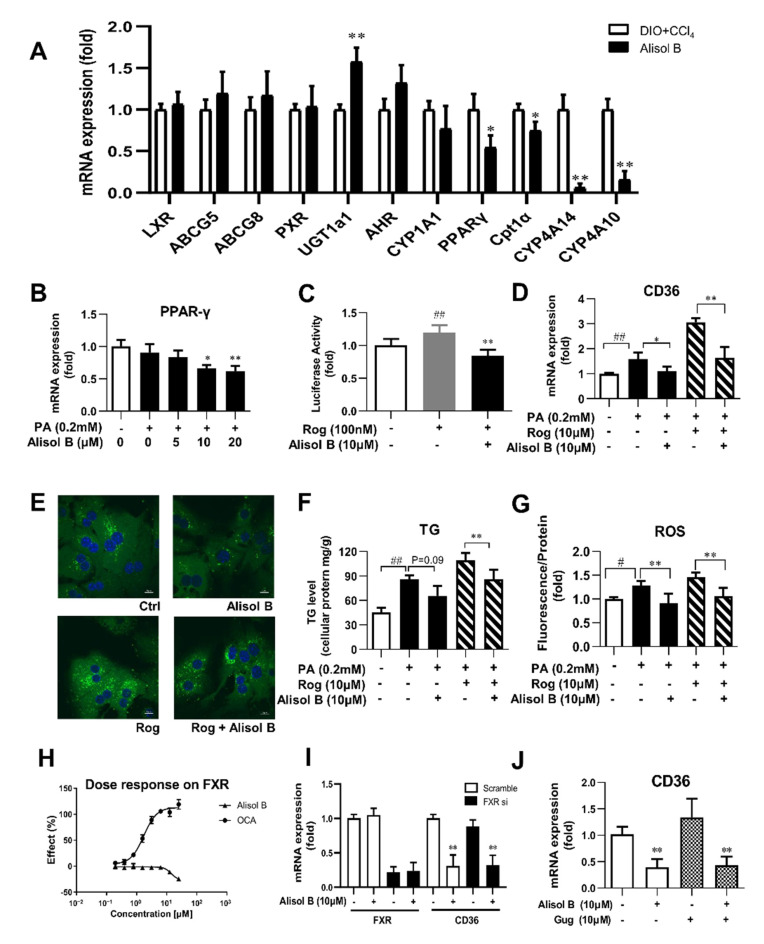
Figure 6.
Alisol B suppressed CD36 expression through downregulating PPARγ, and this effect was independent of FXR. (A) The mRNA expression of hepatic LXR, PXR, AHR, PPARγ, and their target genes were examined in DIO+CCl4-induced NASH mice. (B) The gene expression of PPARγ was measured in PA-induced primary hepatocytes treated with Alisol B. (C) Huh7 cells were transiently transfected and then treated with Alisol B (10 μM) in the presence of Rosiglitazone. The transactivation activity of PPARγ was detected in luciferase reporter assay. (D–G) Mouse primary hepatocytes were treated with Alisol B (10 μM) and Rosiglitazone (10 μM) under PA-stimulated conditions. (D) CD36 mRNA level, € BODIPY-C16 fluorescence (600× magnification), (F) cellular TG, and (G) cellular ROS were evaluated. (H) Huh7 cells were transiently transfected and then treated with Alisol B. The agonistic activity on FXR was detected in luciferase reporter assay. (I) The mRNA levels of FXR and CD36 in FXR knockdown hepatocytes treated with Alisol B (10 μM) were detected. (J) The mRNA level of CD36 in hepatocytes treated with Alisol B (10 μM) in the presence of Gugglusterone (10 μM) was detected. Data in (A) are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 8. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with DIO+CCl4 group. Data in (B–H) are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 5. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 compared with normal control group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with the PA-induced group or Rosiglitazone-induced group. Data in (I,J) are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 5. ** p < 0.01 compared with the normal control group.