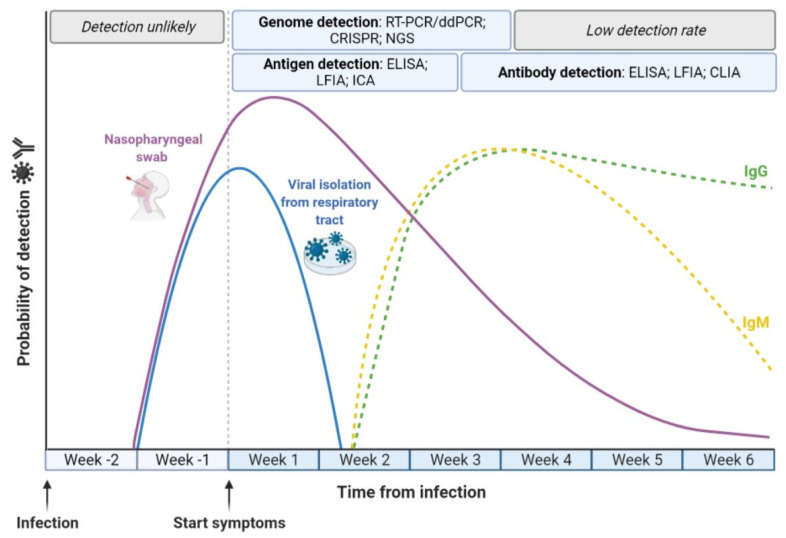
Figure 1.
Progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection and in vitro diagnostics. The detection of active SARS-CoV-2 infection is performed using molecular diagnostics, i.e., real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), droplet-digital PCR (ddPCR), clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), in order to detect the viral RNA during the first weeks after the emergence of symptoms. In this period, it is also possible to detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2 components using antigen-based immunoassays, i.e., the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) and immunochromatographic assay (ICA). Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies (IgG and IgM) occurs through antibody-based immunoassays, i.e., ELISA, LFIA and chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA), from the third week after symptoms.