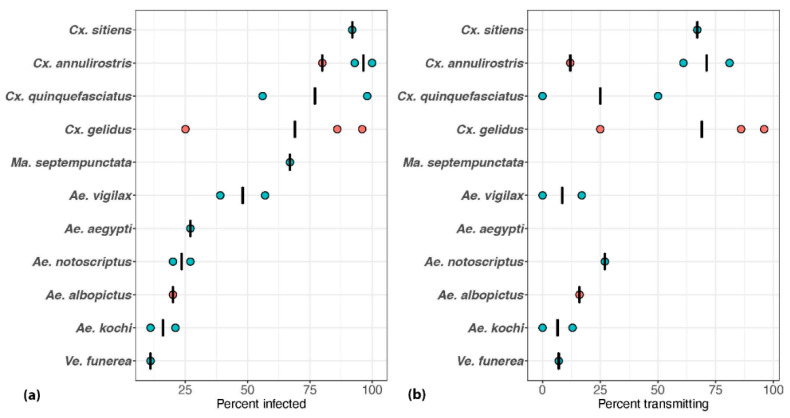
Figure 2.
Results of the vector competence experiments conducted to assess the ability of Australian mosquito species to (a) become infected with and (b) transmit the Japanese encephalitis virus. Mosquitoes were allowed to feed on an infectious blood meal containing 106−7 infectious units of virus per milliliter and tested at days 10–14 post-exposure. The orange and blue circles represent experiments conducted with genotype 1 and genotype 2 viruses, respectively, and the bars represent the means of data derived from separate virus exposures. Previously published studies [45,46,47,48] provided the source data. A minimum of five mosquitoes was required for inclusion in the analysis. Mansonia septempunctata and Ae. aegypti were not tested for their ability to transmit the virus.