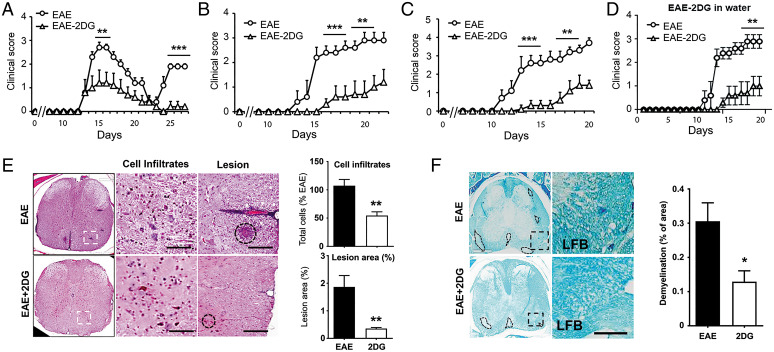
Fig. 4.
Targeting energy pathway ameliorates disease progression in EAE mouse models. (A–C) EAE was induced in SJL, B6, and 2D2 mice using PLP and MOG35-55, respectively. One set of the group was given daily 2DG (50 mg/kg body weight, intraperitoneally in 200 µL volume) and another set was given PBS as vehicle. Clinical score was taken until the end of the study (n = 15 per group). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared with vehicle treated EAE group was considered as statistically significant. (D) EAE was induced in 2D2 mice with MOG and one set was given 2DG in drinking water (0.2 mg/mL; wt/vol) from day 7 postimmunization. Clinical score was taken until the end of the study (n = 6 per group). **P < 0.01 compared with vehicle-treated EAE group was considered as statistically significant. (E, F) Representative images shows histopathological changes in the spinal cord tissues in EAE mice with or without 2DG treatment. Sections were staind with hematoxylin and eosin to show cells infiltration and lesion size and Luxol fast blue to (LFB) to demonstrate changes in myelin content. Data were represented as mean ± SD (n = 6 mice/group). Scale bar, 100 μm. Statistical analyses were done with Student’s t test. Statistical significance was determined at P < 0.05.