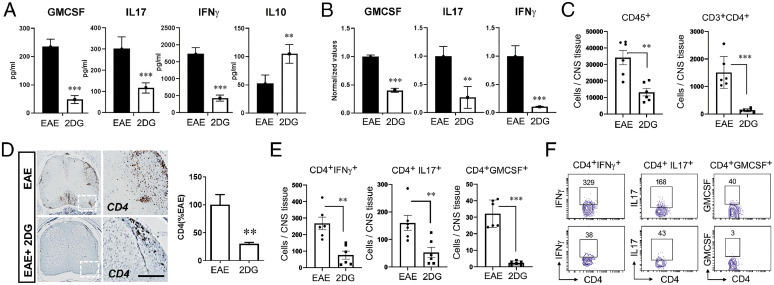
Fig. 5.
Targeting energy pathway moldulates CD4 cells infiltration and response in EAE mouse. (A) On day 20, splenocytes of EAE-treated and untreated with 2DG in drinking water were stimulated with MOG35-55. Post-72 h, proinflammatory (GM-CSF, IL-17 and IFN-ɣ) and antiinflammatory (IL-10) were examined in cell supernatant using their specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The data presented are the mean ± SD of two independent experiments (n = 5 per group). (B) Expression of GM-CSF, IL-17, and IFN-ɣ were examined in splenocytes of both groups using quantitative PCR and normalized with the control gene; ribosomal L27 housekeeping gene. The data presented are the mean ± SD of four values. (C) Quantitation of CD45+ and CD3+CD4+ cell number in the spinal cord and brain of EAE and 2DG treated (drinking water) groups by flow cytometry. The data presented are the mean ± SD of six animals per group. (D) Representative immunohistochemical staining and quantitative analysis for CD4+ T cell infiltration in EAE induced mice with or without 2DG treatment in drinking water. Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 6 mice per group). Scale bar, 100 µm. Statistical analysis was done by Student’s t test. Statistical significance was determined at P < 0.05. (E, F) Quantitation of IFN-ɣ, IL-17α, and GM-CSF producing CD4+ T cell number in the spinal cord and brain of EAE- and 2DG-treated (drinking water) groups. The data presented are the mean ± SD of six animals per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Student’s t test, one-way analysis of variance.