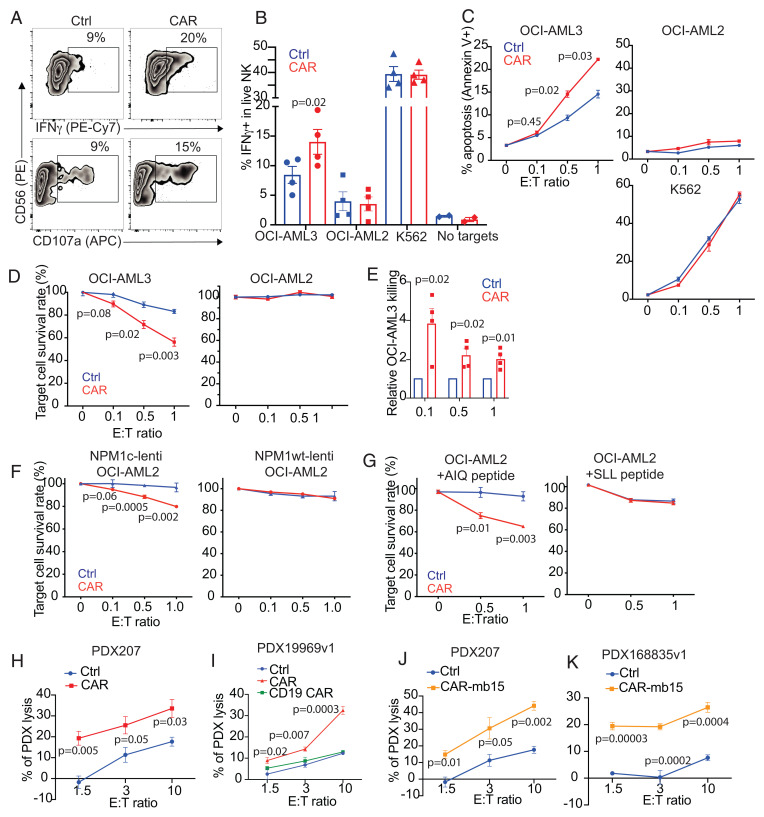
Fig. 3.
NPM1c-CAR CIML NK cells exhibit potent and specific anti-AML function in vitro. (A) Representative flow cytometry staining profiles of IFNγ or CD107a versus CD56 of untransduced (Ctrl) and NPM1c-CAR transduced (CAR) CIML NK cells. Indicated NK cells were cocultured with OCI-AML3 target cells for 6 h and CD56+ cells were analyzed. (B) Summary data showing percentages of IFNγ-expressing cells in CAR-expressing vs. untransduced (Ctrl) CIML NK cells following incubation with OCI-AML3 (NPM1c+ HLA-A2+), OCI-AML2 (NPM1c− HLA-A2+), K562 (HLA−), or no target cells. (C) Killing of OCI-AML3, OCI-AML2, and K562 target cells by untransduced (Ctrl) and CAR-transduced CIML NK cells at the indicated effector (E): target (T) ratios. CIML NK cells and target cells were incubated for 4 h, and percentages of annexin V+ tumor cells were assayed by flow cytometry. (D) Killing of OCI-AML3 and OCI-AML2 target cells by untransduced (Ctrl) and CAR-transduced CIML NK cells at the indicated E: T ratios. CIML NK cells and luciferase-expressing target cells were incubated for 24 h, and luciferase activity was quantified. (E) Summary data showing OCI-AML3 target killing by NPM1c-CAR CIML NK cells as assessed by luciferase assay. Data were normalized to the percentage of killing by the corresponding untransduced (Ctrl) CIML NK cells. (F) OCI-AML2 cells were transduced with lentivirus expressing NPM1c (Lenti-NPM1c, Left Panel) or the wild-type NPM1 control (Lenti-NPM1wt, Right Panel). Transduced cells were sorted, expanded, and used as target cells for killing assays as described in D. Killing of the transduced OCI-AML2 target cells by Ctrl and CAR-transduced CIML NK cells were measured at the indicated E:T ratios. (G) Comparison of killing of OCI-AML2 cells pulsed with 1 μM of AIQ (Left) or SLL (Right) peptides by NPM1c CAR-CIML NK cells or untransduced (Ctrl) CIML NK cells. NK cells were cocultured with peptide-pulsed OCI-AML2 target cells at the indicated E:T ratios for 24 h. Target cell killing was measured by the luciferase activity of surviving target cells. (H) Killing of low-passaged NPM1c+ HLA-A2+ PDX AML target cells by NPMc1c-CAR CIML NK cells in comparison with their untransduced CIML NK cells from the same PB donor (n = 1 PDX donor and 1 PB donor for each graph; error bars from technical triplicates). (I) Killing of NPM1c+ HLA-A2+ PDX AML target cells by untransduced (Ctrl), NPM1c CAR-CIML (CAR), and irrelevant CD19 CAR CIML NK cells. (J and K) Killing of NPM1c+ HLA-A2+ PDX target cells by NPMc1c-CAR-mb15 CIML NK cells (n = 2 PDX donors and 2 PB donors). Each dot in B and E represent one different PB donor. n = 4 in B and E. Error bars in B and E represented mean with SEM. Error bars in C, D, and F–K represented mean with SD from 3 to 5 technical replicates. Data were analyzed by two-tailed paired Student’s t test (B), two-tailed one sample t test (E), and two-tailed unpaired t test (C, D, and F–K). Data are pooled from two (B and E) independent experiments, or representative of three (C, D, F, and G) independent experiments.