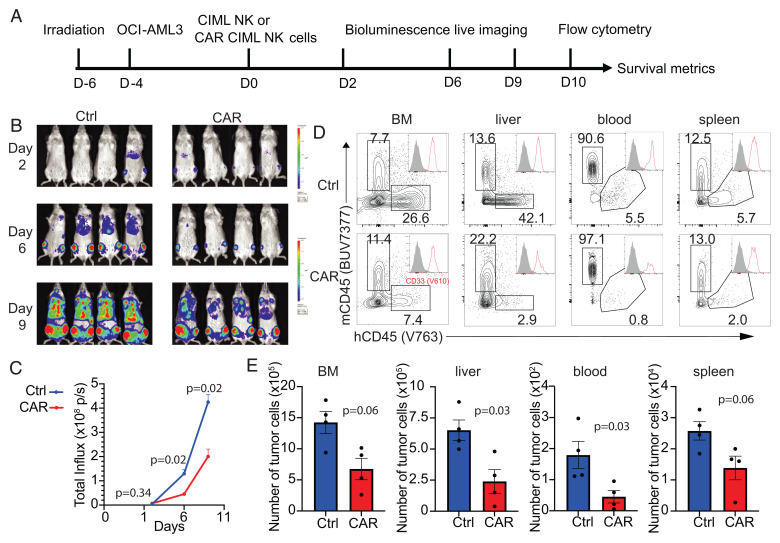
Fig. 4.
NPM1c-CAR CIML NK cells are effective in controlling AML in vivo in a xenograft model. (A) Scheme of the experimental setup. NSG mice were sublethally irradiated, and 2 d later, luciferase+ OCI-AML3 cells (5 × 105 cells) were injected IV. After 4 d, 1 × 106 untransduced or transduced CIML NK cells were injected IV into the tumor-bearing mice. BLI was performed on the indicated days to monitor tumor burden. Mice were euthanized at 10 d post-NK cell adoptive transfer for flow cytometry analysis. (B and C) Comparison of tumor burden in recipient mice given untransduced (Ctrl) and transduced (CAR) CIML NK cells by BLI (B) and quantification of luciferase activity (C). (D) Representative flow cytometry staining profiles of hCD45 versus mCD45 gating on live cells in the indicated tissues. Inserts show CD33 histogram of hCD45+ cells. (E) Summary data showing absolute numbers of leukemic cells in the indicated tissues of recipient mice at day 10 after adoptive transfer with untransduced CIML (blue) vs. NPM1c CAR CIML NK cells (red) (n = 4 mice per group). Error bars in C and E represented mean with SEM. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with the Sidak posttest (C) or two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (E). Data are representative of three (B–E) independent experiments.