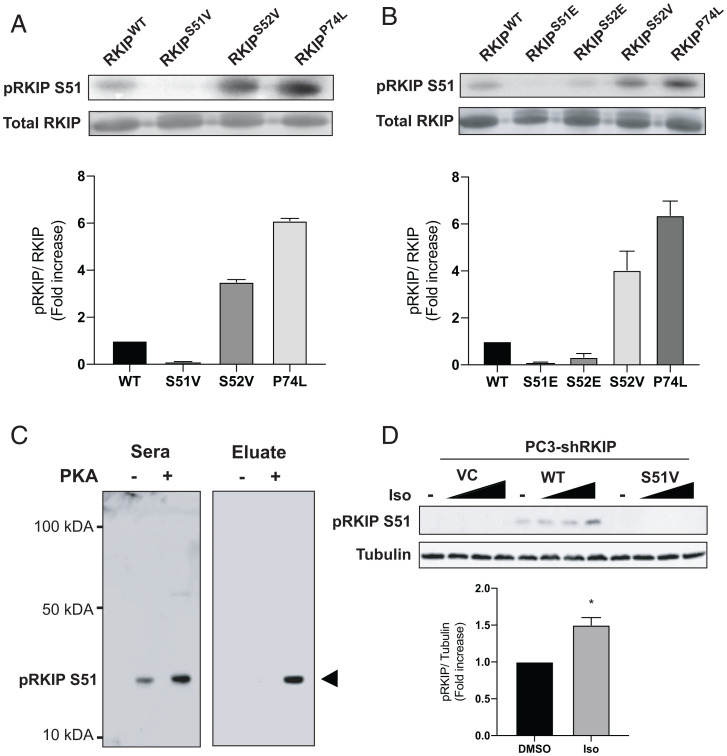
Fig. 1.
Phosphorylation of RKIP by PKA. (A and B) Purified RKIP proteins were tested for in vitro kinase assays. After immunoblotting with anti-RKIP antibody, the phosphorylation levels were quantified using ImageQuant 5.2 software and normalized to RKIP protein levels to compare the phosphorylation between the various mutants. The fold induction shown in the bar graphs is an average of three experiments, and the error bars indicate SEM. (C) Immunoblotting purified WT (PKA-) and PKA-phosphorylated RKIP (PKA+) with unfractionated anti-pS51 antiserum (Sera) and purified antibody (Eluate). Rabbit serum was purified on an anti–phospho-S51 RKIP peptide column as described in Materials and Methods. (D) Immunoblotting of lysates from PC-3 prostate cancer cells treated with isoproterenol (Iso). PC-3 cells that had been stably depleted of RKIP by expression of human RKIP shRNA were transfected with a control vector (VC), RKIPWT, or the S51V RKIP mutant. Cells were lysed, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-pS51 RKIP antibody or anti-tubulin antibody. For isoproterenol treatment, cells were serum-starved for 20 h and then either treated with DMSO or stimulated with 0.005, 0.05, or 1 μM isoproterenol (Iso) for 10 min. Cells were lysed, and lysates were immunoblotted with anti-pS51 RKIP antibody or anti-tubulin antibody. The protein bands were quantified using Licor ImageStudio, and the results were plotted for pS51 phosphorylation relative to tubulin. Mean values from four independent experiments were plotted, and P values were obtained using a Student’s t test. *P < 0.05.