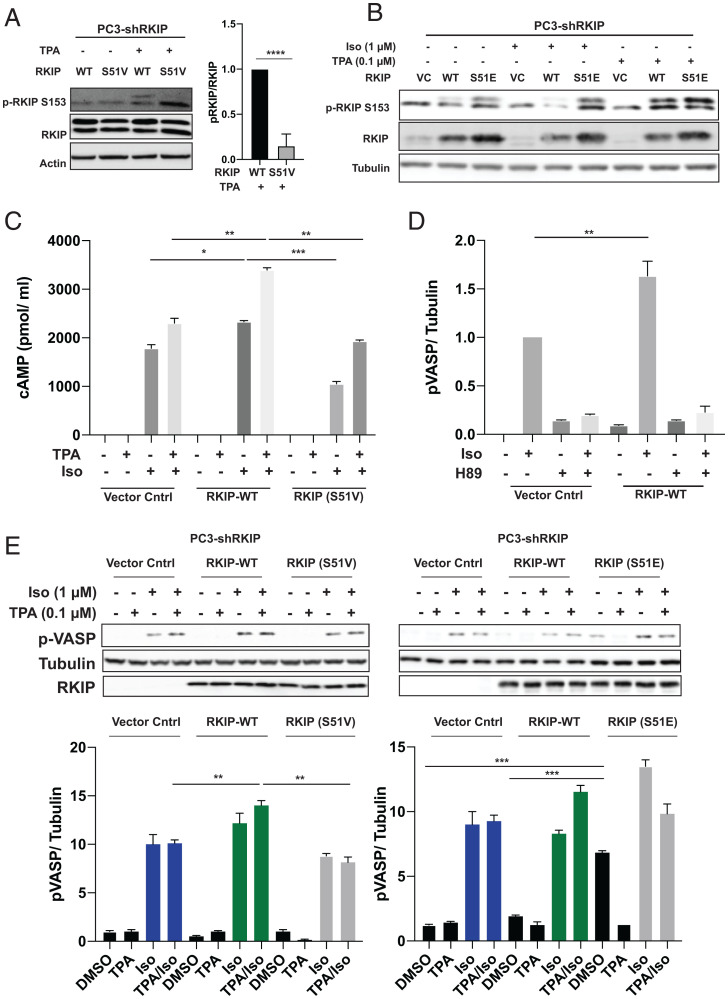
Fig. 2.
PKA phosphorylates RKIP at Serine 51, increasing both PKC phosphorylation of RKIP at Serine 153 and PKA activity in prostate tumor cells. For A–E, PC-3 cells stably expressing RKIP shRNA were transfected with control vector (VC), WT, or mutant RKIP (S51V, S51E) and serum-starved for 20 h before stimulation using TPA for 30 min, isoproterenol (Iso) for 10 min, or H89 for 30 min as indicated. (A) Phosphorylation of RKIP and mutant S51V RKIP at S153 in PC3 cells after TPA treatment. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-pS153 RKIP antibody or anti-Actin antibody and quantified for plots. The lower band on phosphorylated RKIP and RKIP blots is nonspecific. (B) Phosphorylation of RKIP and mutant RKIP S51E at S513 after TPA and Iso treatment in PC3 cells. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-pS153 RKIP antibody, anti-RKIP antibody, or anti-tubulin antibody. (C) Phosphorylation of S51 RKIP enhances cAMP levels in prostate tumor cells. Total cAMP levels were quantified as in Materials and Methods. (D) Phosphorylation of S51 RKIP enhances PKA activity in prostate tumor cells. Cell lysates were assayed for PKA activity by immunoblotting with anti-pVASP antibody. Samples were normalized to tubulin by immunoblotting with anti-tubulin antibody. (E) An S51V mutant reduces activation of PKA in TPA/Iso-stimulated cells, and S51E potentiates activation of PKA. Cell lysates were assayed for PKA activity by immunoblotting with anti-pVASP antibody. Samples were normalized to tubulin by immunoblotting with anti-tubulin antibody. Samples were quantified using Licor ImageStudio. Mean values from three independent experiments were plotted, and P values were obtained using a Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.